Subject
Subject is the base of data analysis on certain perspective, let's follow this chapter to build a subject.
Structure
Firstly, define structure of subject. Topics included in connected-space are available here, simply follow the wizard,
-
Step 1, pick topics,
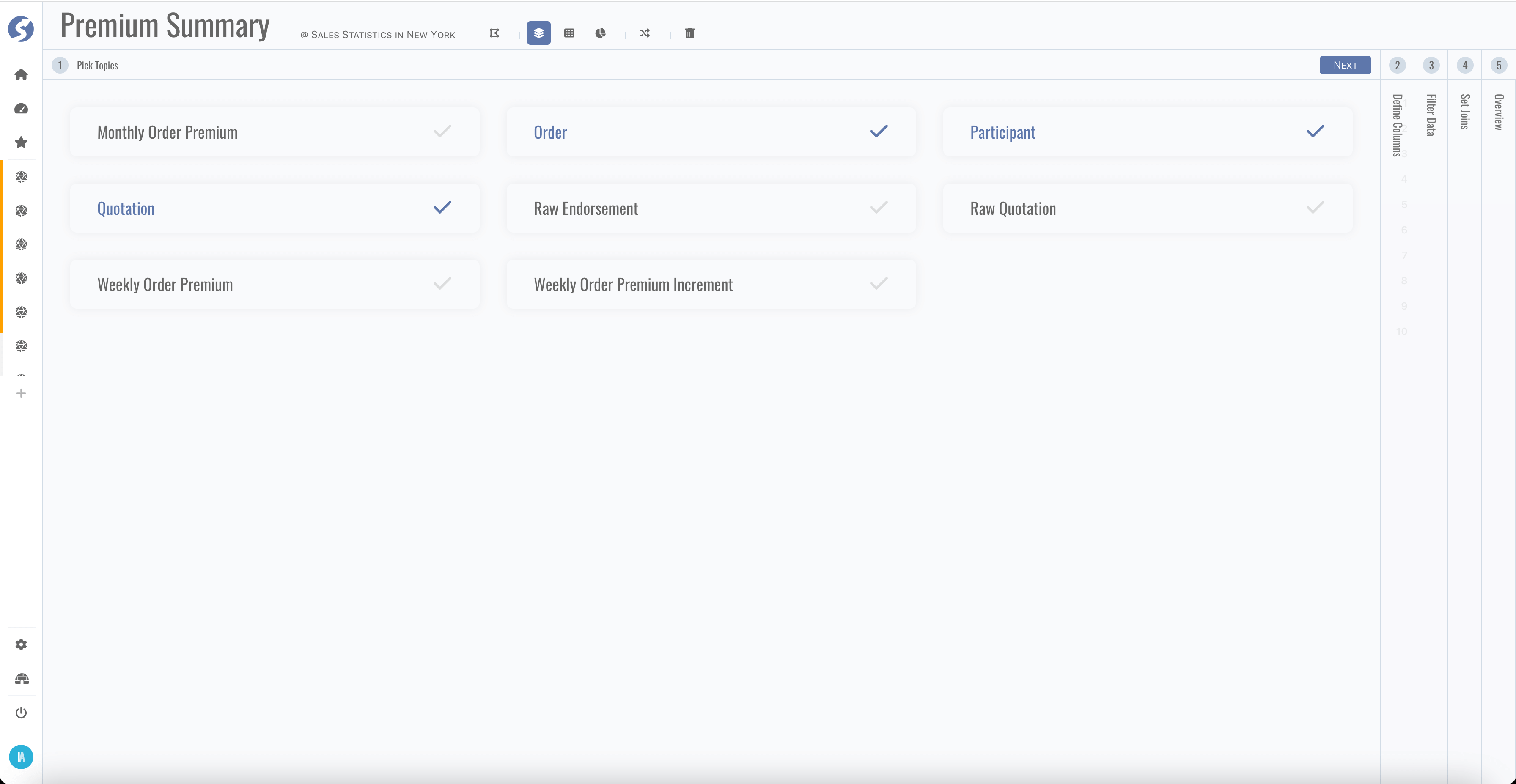
-
Step 2, define columns,
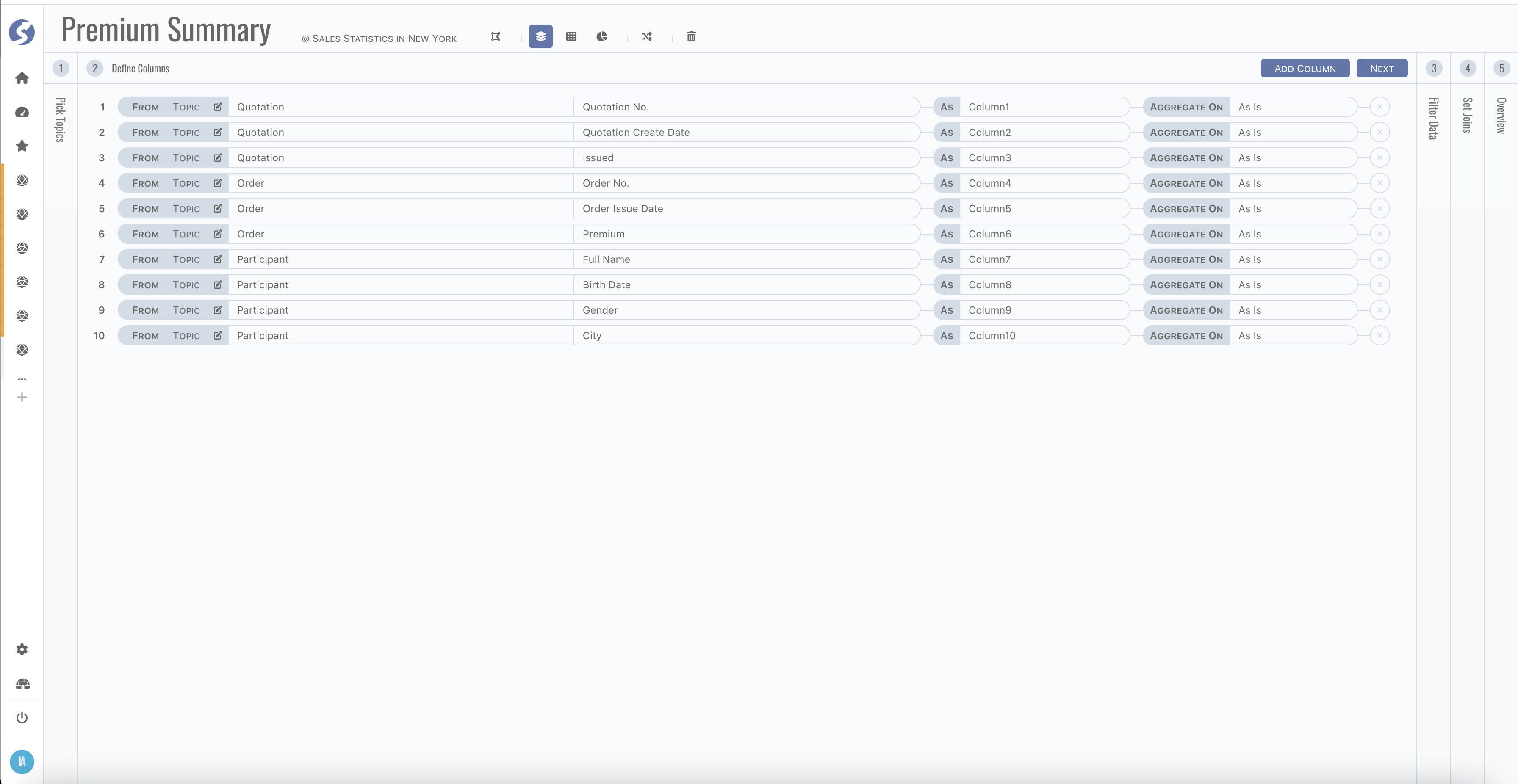
Column can be from,
- a topic directly,
- or a constant value,
- or computed by functions.
There are several functions are supported for computation,
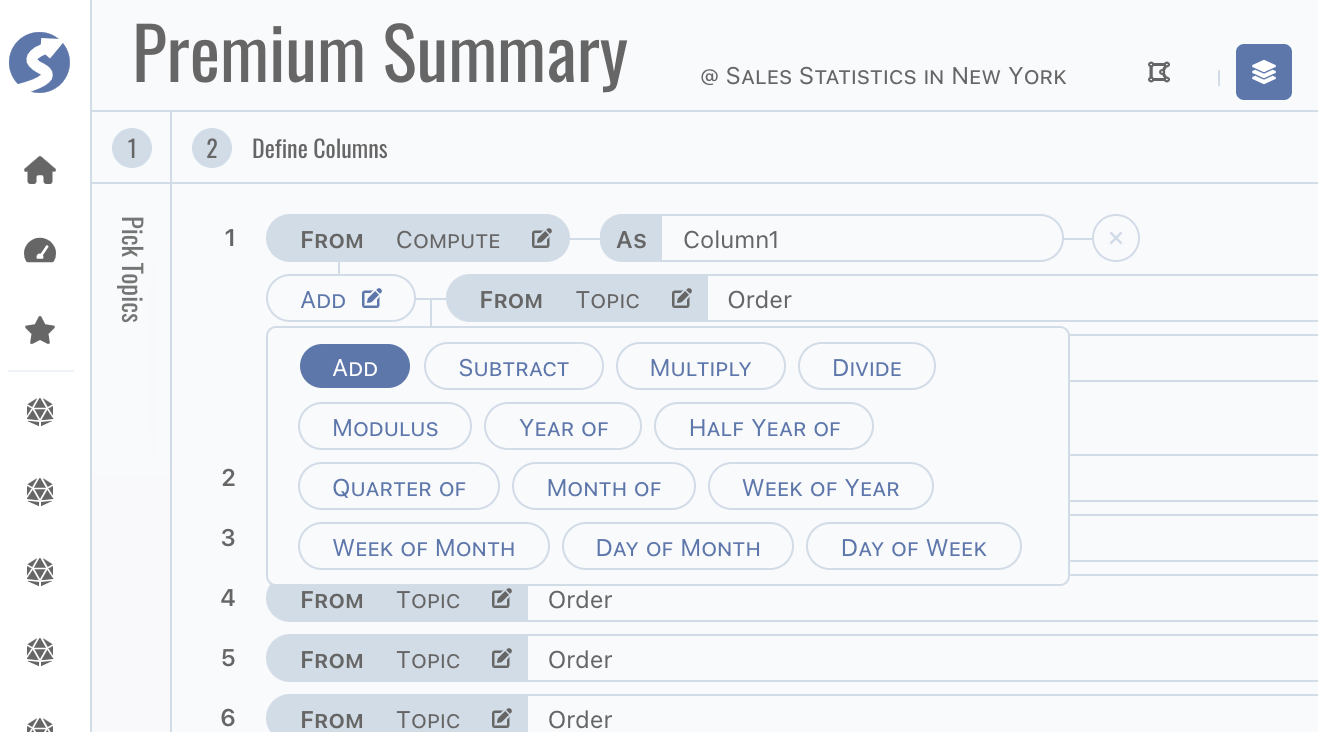
Column also can be aggregated by one of
count,sum,avg,maxandmin. If any column is configured as aggregation, dataset should be grouped by other non-aggregation columns.tipGive a friendly name to each column.
tipCompute functions supported by pipeline also are supported by subject.
-
Step 3, define filters,
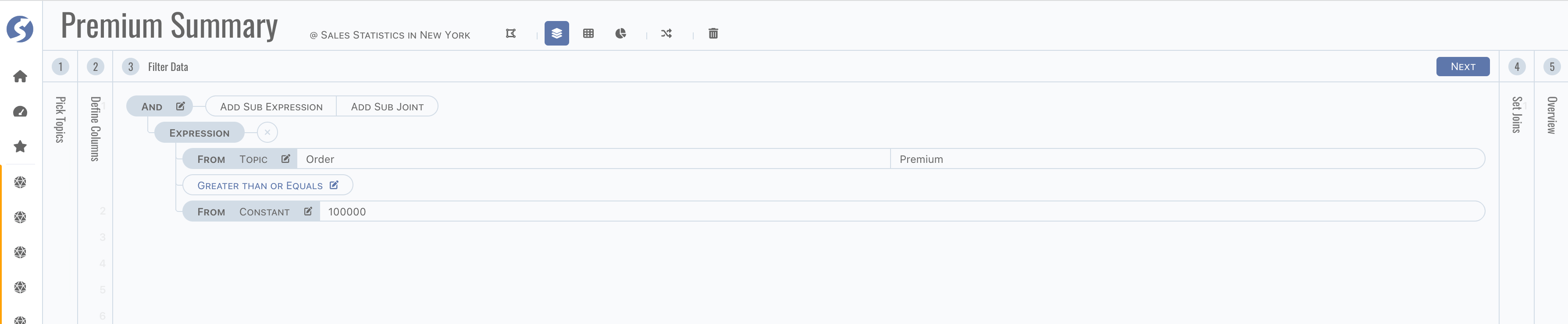 tip
tipFilters are applied for each report in this subject.
-
Step 4, define joins when two or more topics included,
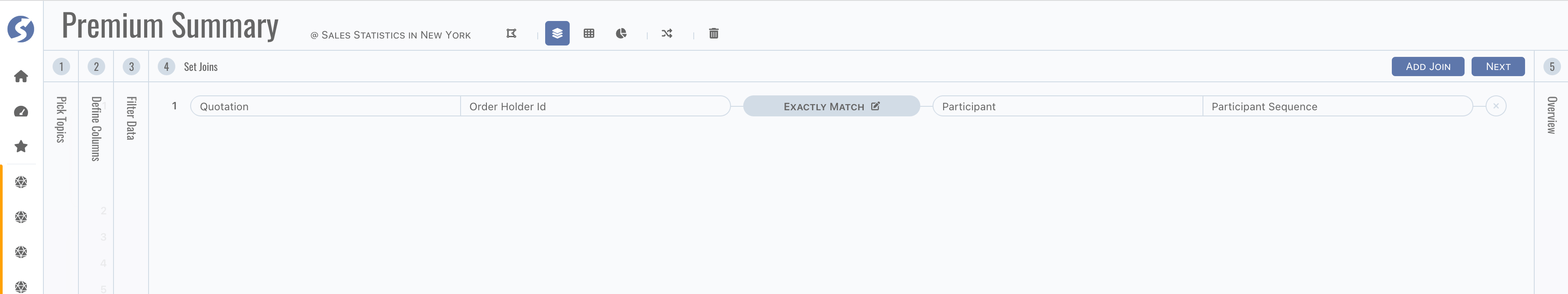 tip
tipJoins are not needed when only one topic is used in subject.
Depending on type of join, data searched out contains
- Intersection of both sides when it is
Exactly Match, - Left side and right side in intersection when
Left Side Prioritized, - Right side and left side in intersection when
Right Side Prioritized.
- Intersection of both sides when it is
-
Finally, view definition dsl,
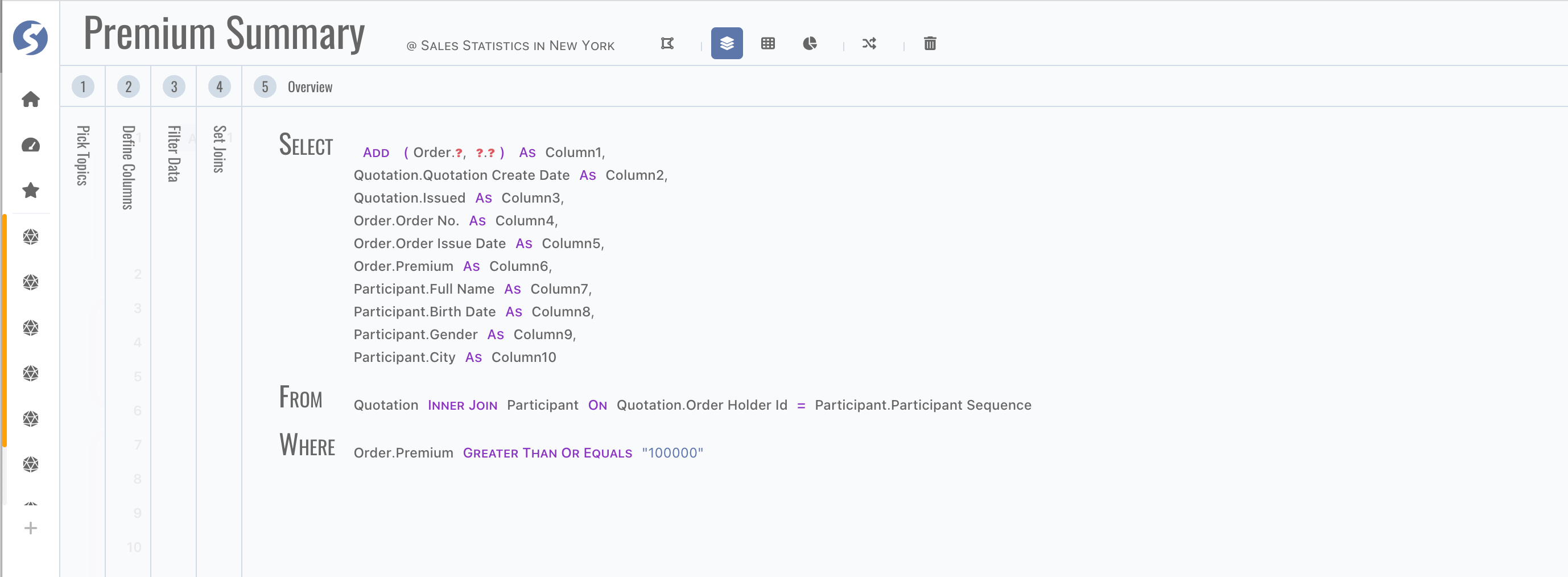 tip
tipRed question mark means something incorrect.
Dataset
After structure defined, move to dataset page,
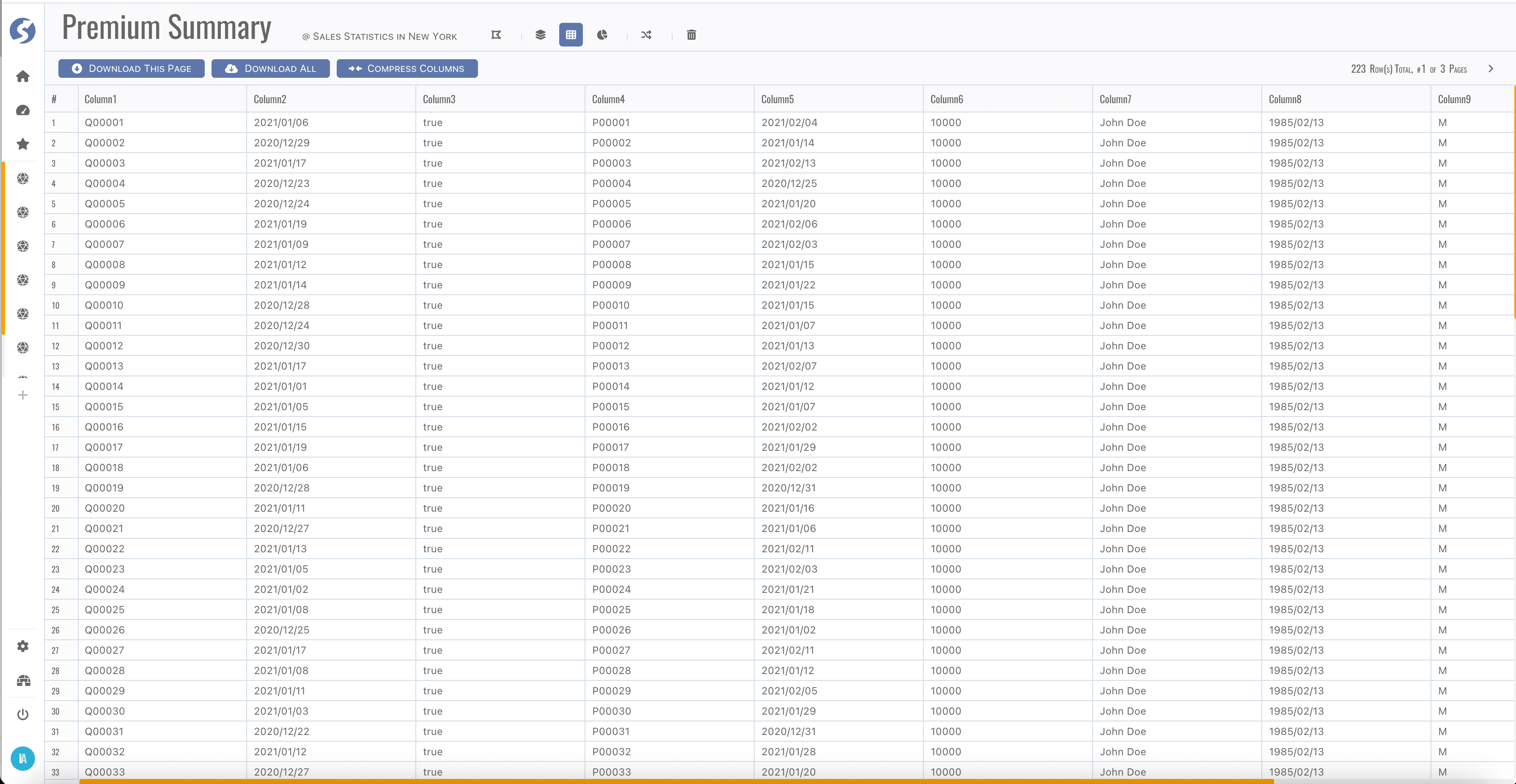
It is a pagination grid, page switcher is on top-right corner. Check data, make sure they are what you imaged.
There is a count limitation for download all data, check Doll for more details.
Columns can be resized, sorted, drag-and-dropped and locked to left.
Reports
Everything is OK now, let's goto reports page,
Header
By click header buttons,
- Back to connected-space,
- Switch between structure/dataset/reports of current subject,
- Create new report,
- Switch to another subject,
- Delete current one.
And change subject name by click name part in header.