Pipeline Service
Pipeline service is the core of watchmen, topic data is processed, transformed and aggregated through pipelines which are predefined. Before go through the services and rest apis, let's learn about pipeline itself first.
Pipeline
A pipeline is made up of the following materials:
- A prerequisite to decide current pipeline should be triggered or not,
- A set of stages to process trigger topic data. For each stage, including,
- A prerequisite to decide current stage should be run or not,
- A set of units to process data. For each unit, including,
- A prerequisite to decide current unit should be run or not,
- A loop variable (from memory variables) to decide current unit is process a list or a single data,
- A set of actions to process data. There are different types of actions are built-in:
- Alarm action,
- Copy to variable action,
- Read row action,
- Read rows action,
- Read factor action,
- Read factors action,
- Exists action,
- Write row action,
- Insert row action,
- Insert or merge row action,
- Write factor action,
- Delete row action,
- Delete rows action.
To learn how to define a pipeline, visit here for more details.
Pipeline Kernel and Surface
A set of services and rest apis are provided by pipeline kernel and surface.
Pipeline Trigger
Trigger a pipeline can be triggered synchronized,
curl \
--location \
--request POST 'http://host:port/pipeline/data?topic_name=a_topic&tenant_id=1' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ...' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"code": "a_topic",
"data": {
...
},
"triggerType": "insert-or-merge",
"tenantId": "1",
"traceId": "1"
}'
code: topic name, case sensitive,data: a JSON object, topic data,triggerType: type of trigger,insert,merge,insert-or-mergeanddeletetenantId: required when current user is super admin,traceId: provide only when client wants to control the trace id, otherwise engine will generate one if it is null or undefined.
Or can be triggered asynchronized,
curl \
--location \
--request POST 'http://host:port/pipeline/data/async?topic_name=a_topic&tenant_id=1' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ...' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"code": "a_topic",
"data": {
...
},
"triggerType": "insert-or-merge",
"tenantId": "1",
"traceId": "1"
}'
Compiled Pipeline and Cache
For performance consideration, pipeline is compiled on first invoking. Pipeline kernel caches compiled pipeline with same lifecycle of pipeline itself.
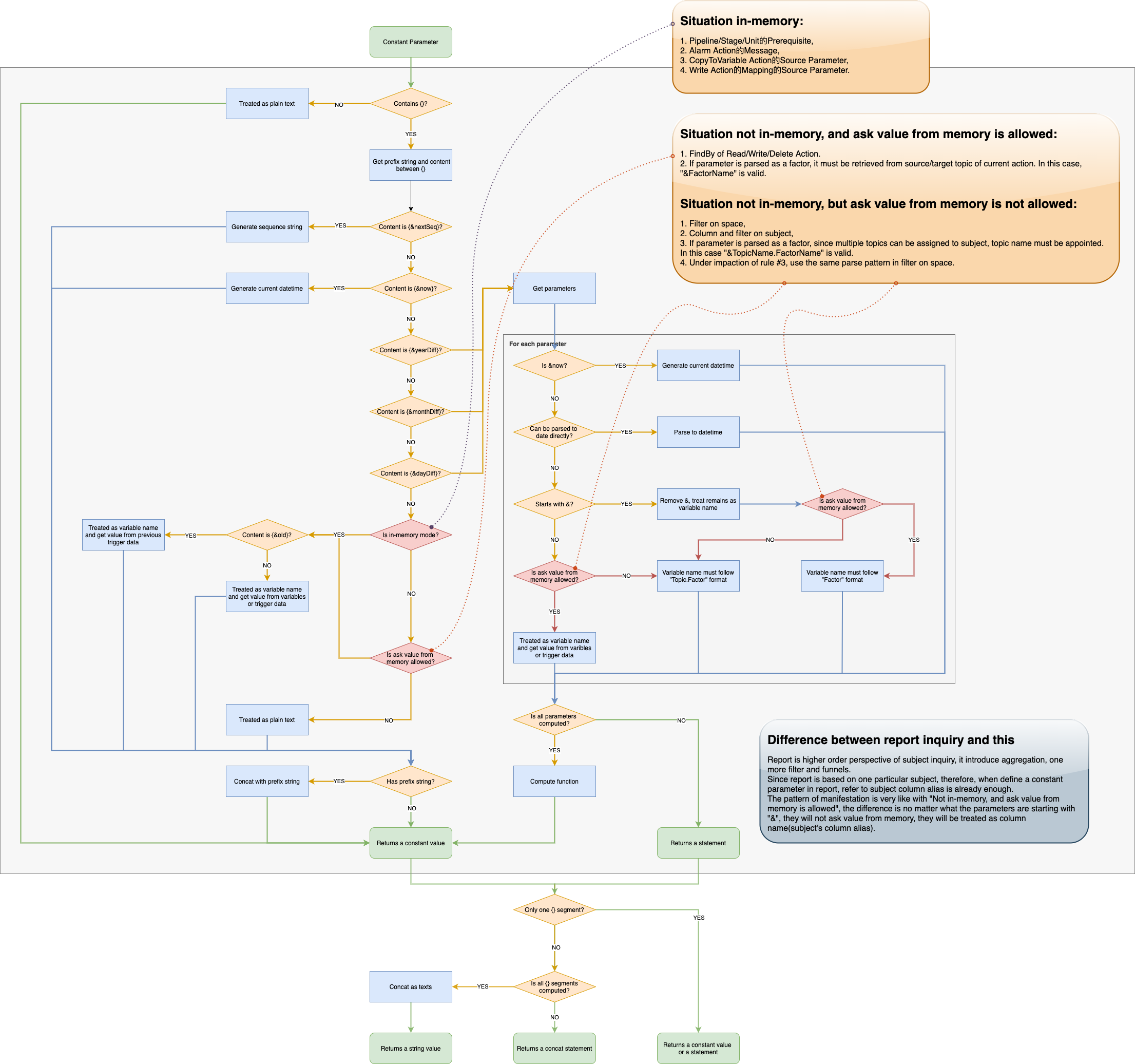
Parse Constant Parameter
It is very complex to parse and give the semantic to a constant parameter value string, following graph explains how to parse a constant parameter in different situations step by step.
Decryption for Factor Value
Factor can be defined with an encryption, and in pipeline, data is read from storage into memory. Sometimes, the encrypted data must be
decrypted, in this case, to enable the DECRYPT_FACTOR_VALUE, kernel will do decryption on read factor/factors/row/rows action.
Decryption feature can be enabled only on pipeline processing, which means it will not be decrypted on retrieve topic data directly.
Alarm Action
In the default implementation, there is only logging for alarm action, on error level with following format:
[PIPELINE] [ALARM] [SEVERITY] MESSAGE
Scan the log file to detect alarm by external services, such as filebeat.
Retry on Insert or Merge Row
If insertion is failed when do insert-or-merge-row action, typically it is caused by an unique index conflict exception. Kernel will try
to do modification, and the logic is exactly same as merge-row.
Retry on Aggregation Topic
To avoid aggregation topic resource contention, there is an additional version property for each aggregation topic. In high concurrency scenarios, version optimistic lock conflict might be occurred. In this case, write action will do modification retrying, and if all retrying is failed, the last retry will use pessimistic lock to ensure success. Visit here for more details about the retry settings.
External Writers
There are two built-in external writers:
- Standard restful writer,
- Standard Elasticsearch writer.
Rest Writer
Like the following curl command,
curl \
--location \
--request POST 'some_url' \
--header 'Authorization: PAT ...' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"code": "eventCode",
"currentData": {
...
},
"previousData: {
...
},
"triggerType": "insert-or-merge"
}'
Elasticsearch Writer
(under construction)
Extend External Writer
To extend an external writer,
Fork our repo, for server side,
- Find
init_prebuilt_external_writersinwatchmen-pipeline-kernel, build your own just follow standard restful writer, - Register it,
- Bingo!
For defined new external writer type in web client, you need to,
- Add data source types into
ExternalWriterType, which inexternal-writer-types.ts, - Add dropdown label into
ExternalWriterTypeInput, which inexternal-writer-type-input.tsx, - Bingo!