Pipeline
Pipeline describes the data flow between topics, triggered by topic data inserted or updated.
Pipeline is available for Admin only.
Catalog Page
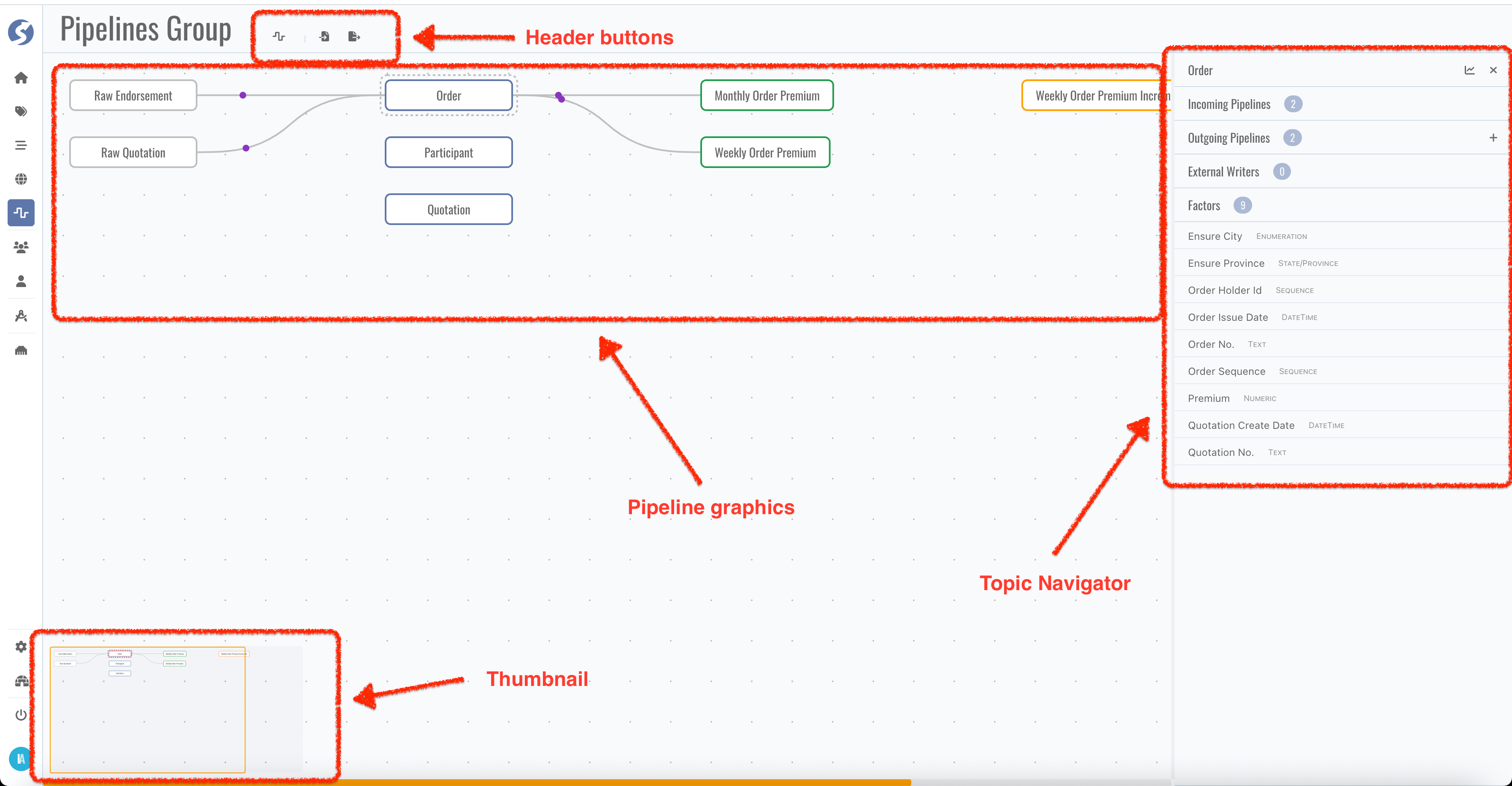
In the very first pipeline catalog page, all existing topics will be displayed and layout automatically.
- Topic blocks can be dragged and dropped anywhere,
- If there are many topics cannot be rendered in one page, use thumbnail to move.
Catalog belongs to the user, it is not shared between users. Topics can be organized individually for every administrator, don't worry about to influence or affected by others.
In pipeline catalog, catalog/graphics/group are the same concept: a set of topics, rendering to a graphics.
Header Buttons
There might many topics, it is too many to show in one graphics, topics can be separated to multiple graphics. Click New Pipeline Group in
header buttons to create a new catalog page.

In a new catalog page,
-
Pipeline catalog name is auto generated, click name part to change it,
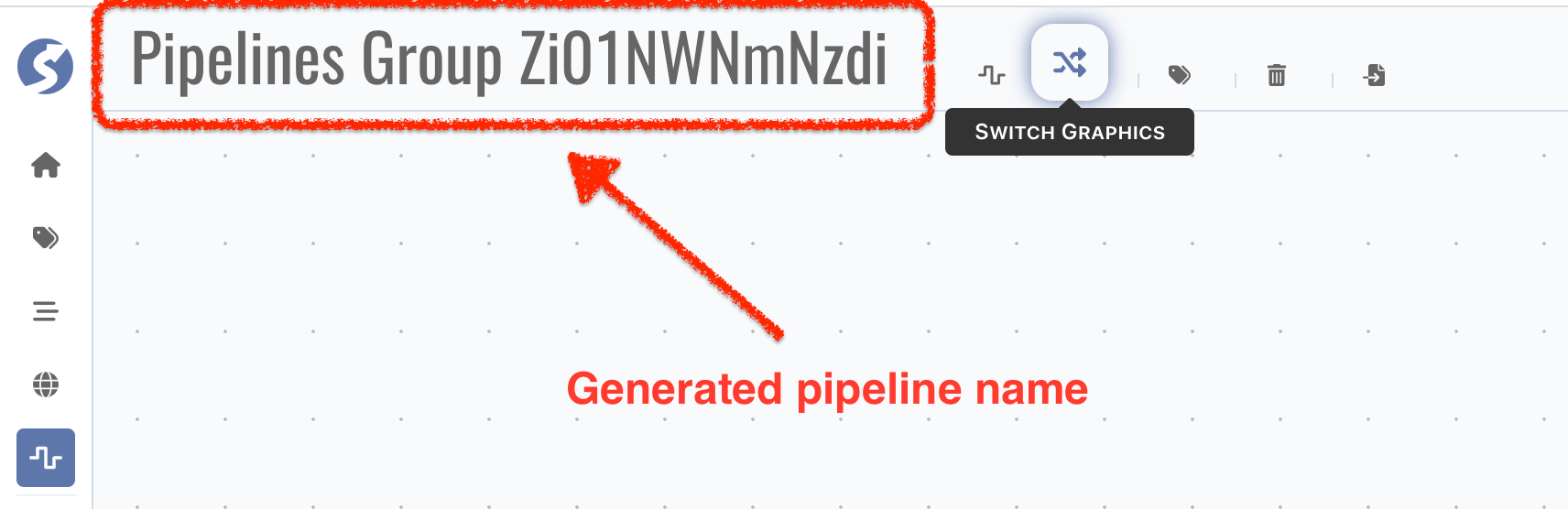
-
No topic selected in the first, click
Pick Topicsto pick topics which you want to render in this catalog,
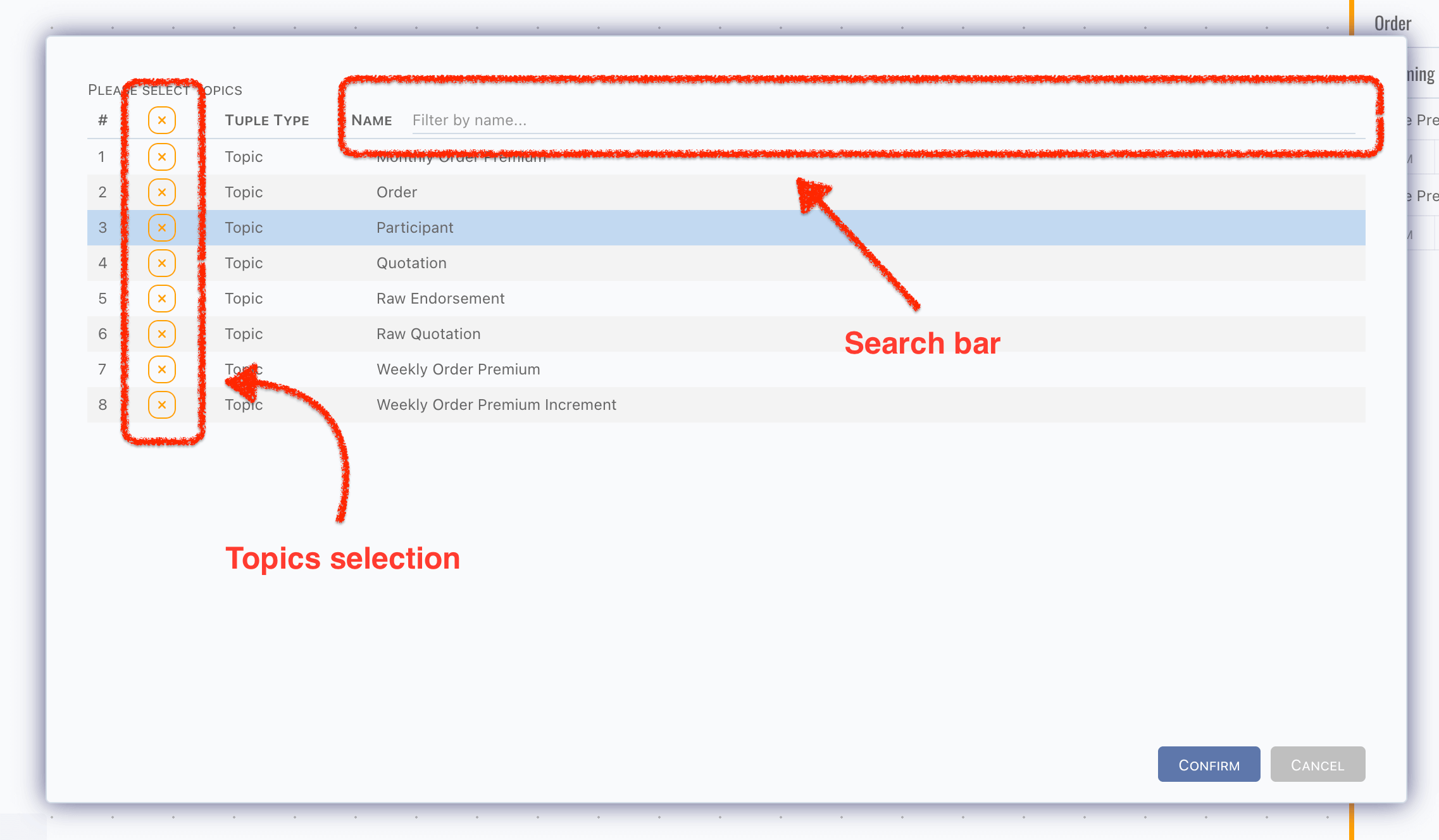 caution
cautionIf topic are not picked on current catalog, pipelines which triggerred by it or write data to it also will be rendered in this catalog.
-
Click
Delete Meto delete current catalog,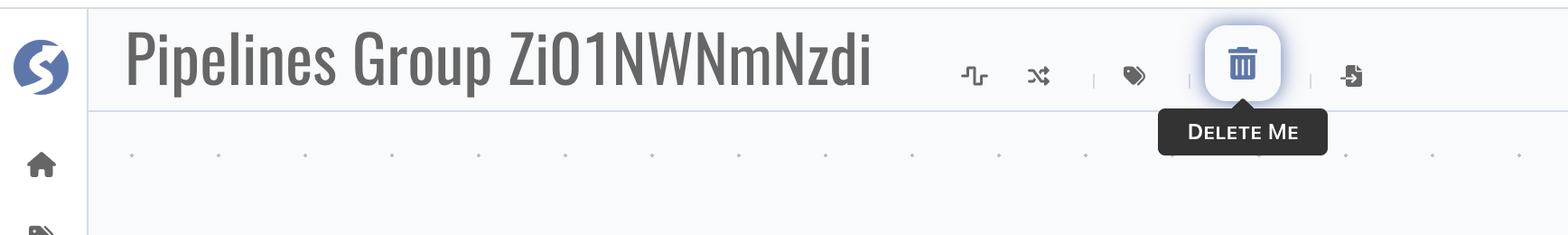 info
info- Topics will not be deleted when delete pipeline catalog,
- The last catalog cannot be deleted.
cautionCatalog cannot be recovered after deletion.
-
Click
Switch Graphicsto switch to another catalog,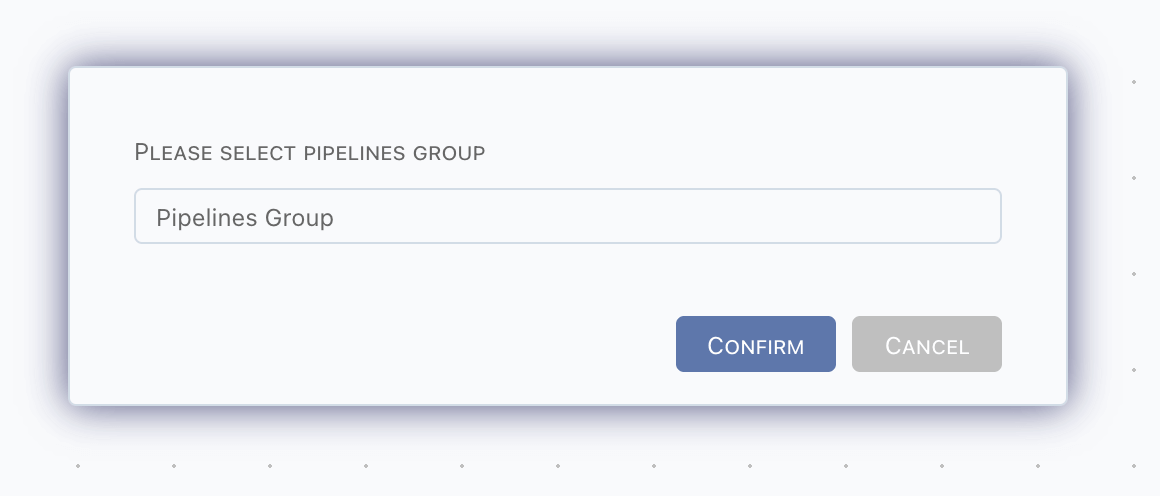 info
infoSwitching is enabled only when there are more than 1 catalog.
Export & Import
Topics, pipelines and other tuples related can be exported as a zip file, by click the Export button in header buttons, a dialog shows,
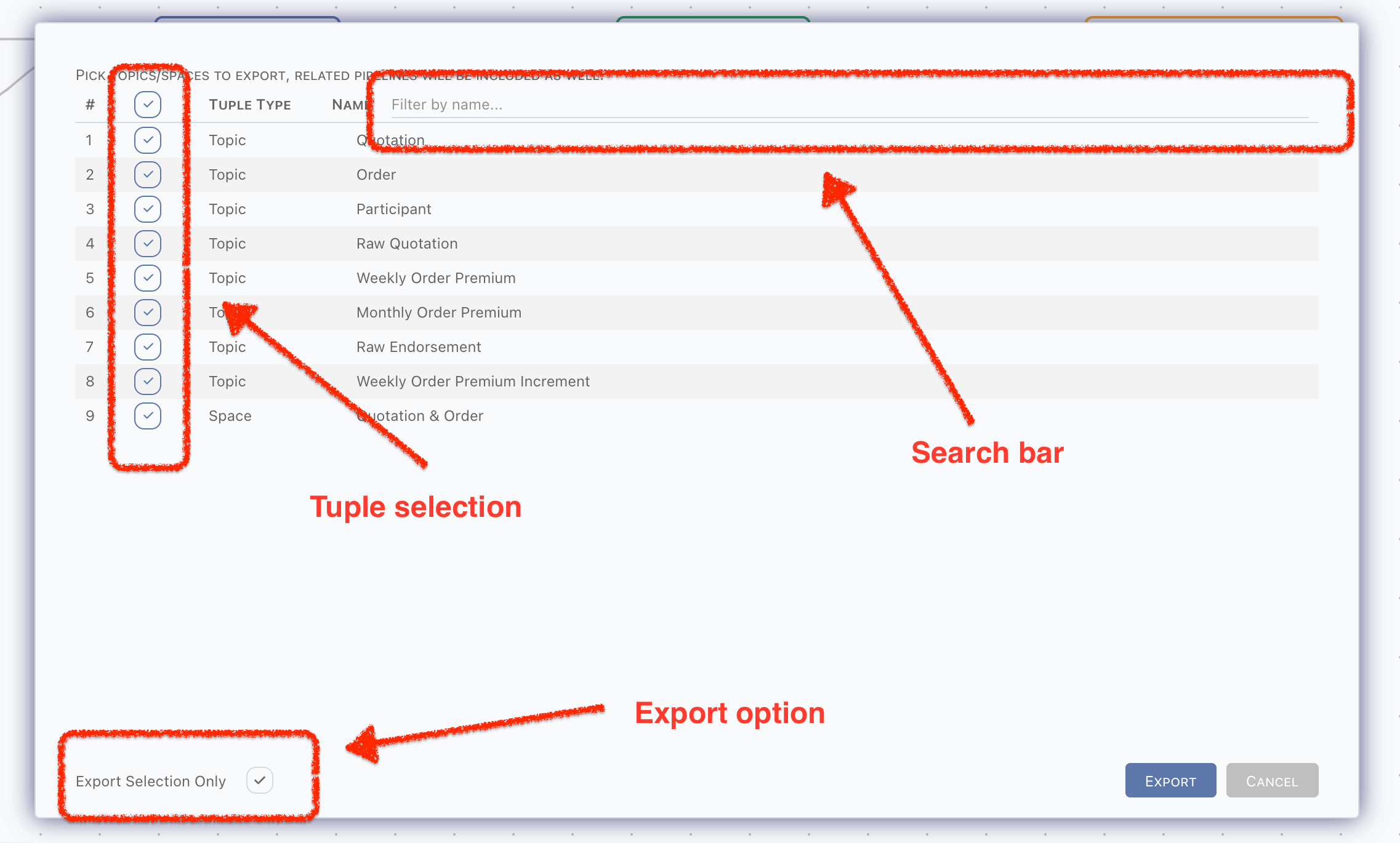
- All topics and spaces are available in export dialog,
- Topics assigned to space will be selected automatically when space is selected,
- Topic not selected will not be packed into zip,
- Or topics relevant will be packed when
Export Selection Onlyis unpicked,
- Or topics relevant will be packed when
- Monitor rules on selected topics will be packed into zip,
- Rules use another topic, and the related topic is not included, will be excluded,
- Space will be deselected automatically when topic within it is deselected,
- Any tuples included by space will be packed into zip according to selected spaces.
- Pipelines will be packed into zip only when,
- Triggerred topic is selected,
- Topics receive data from this pipeline are selected.
There is only one file in this zip,
zip root/
└── Pipelines Group.md
Markdown file cannot be triggered as a file downloading in browser, so we pack it to a zip.
Markdown file is exactly a document for these tuples, it is useful to show the structures. It can be opened by any markdown tool, we recommend using VSCode, with markdown plugins installed. Also, it can be generated to a pdf file, for more easy to read and spread.
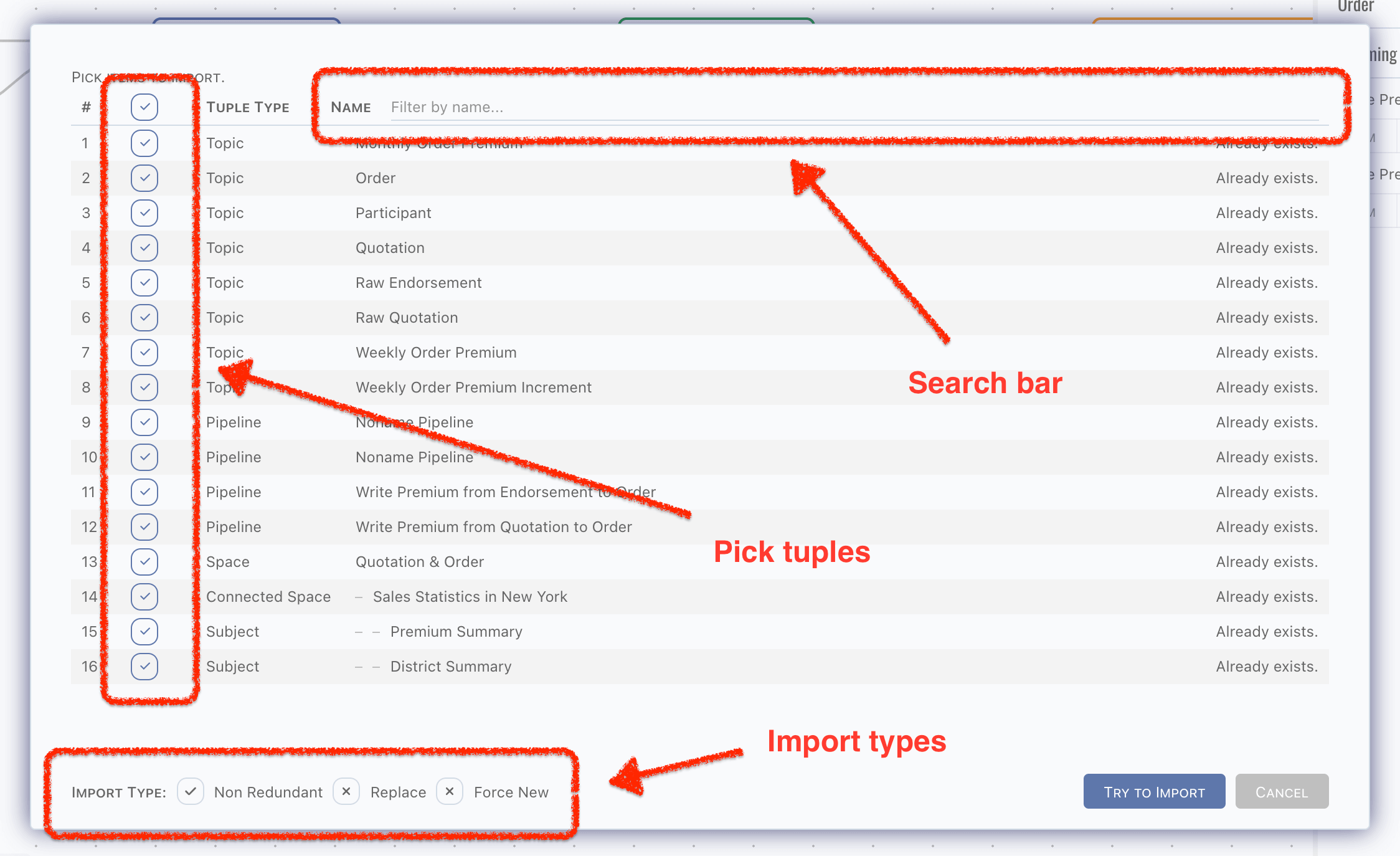
The exported markdown file can be imported again, simply by clicking the Import,
DO NOT modify the hyperlink parts in exported markdown file, it contains the data part. Actually we only read these parts in importing.
Any others are for read only, you can modify them to anything you prefer. But it is not recommended that any modification on not-description
parts, such as factors tables, pipeline DSLs.
In markdown, graphics and images are stored by standard HTML tags, they cannot be rendered correctly in GitHub, Gitlab and some other SaaS services (or private installations). Simply leave them as they are, it is just for security reason. Open it via locally markdown tool, it can be rendered correctly.
There are 3 ways to import data,
- Non-Redundant: existing data will be ignored, and do creation when not existed,
- Replace: existing data will be replaced, and do creation when not existed,
- Force New: treat all imported data as new ones. Ids of tuples will be reset.
Choose the right import way for your scenario and be careful with the imported tuples. Duplication check is based on the ids of tuples, such
as topicId or pipelineId, which means even they have the same name, still will be treated as different ones by importation handler. It
depends on the existing and import tuples, we cannot know what exactly the scenario is, all we can say is it occurs in all 3 ways.
Most of tuples will not create physical entities, but not for topic. Topic name equates table/document name in data source, therefore when topic names are duplicated but have different topic ids, unpredictable exceptions should be raised when do data source objects creation or modification. Be very careful with it after importing.
Topic Navigator
Click navigator panels to view more details of topic,
- Incoming pipelines: pipelines write data to current topic,
- Outgoing pipelines: pipelines triggerred by current topic,
- External writers: triggerred by current topic only, which means external writers in incoming pipelines will not be displayed,
- Factors.
Click Open Pipeline button to edit pipeline,
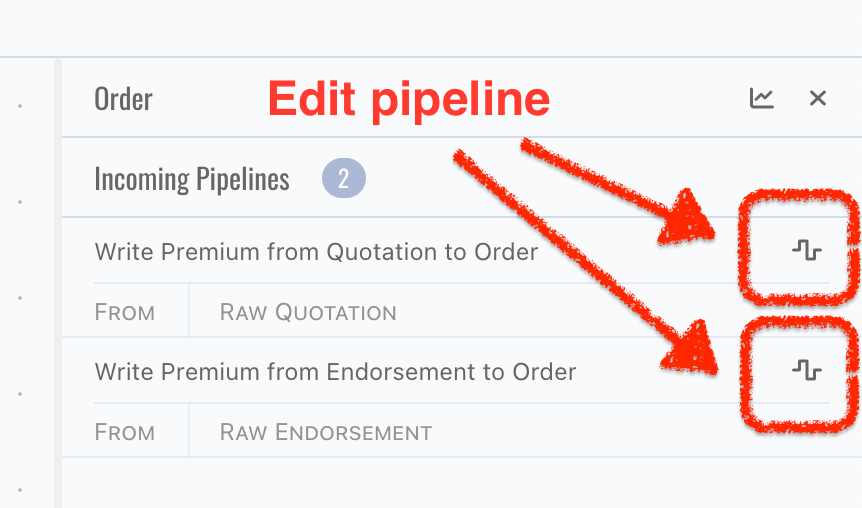
or click Create Outgoing Pipeline button, a new pipeline triggered by this topic will be created,
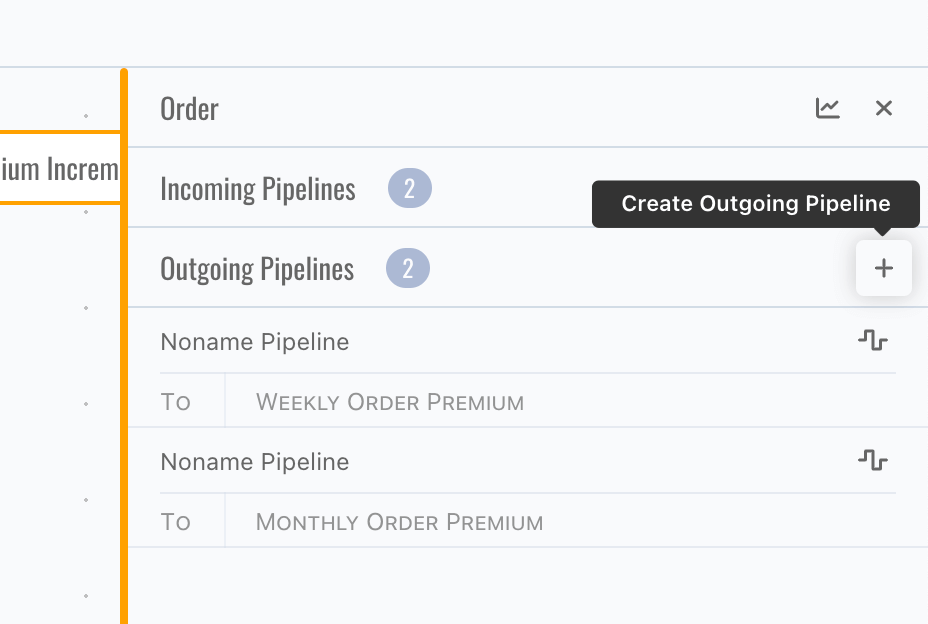
There is no create button for incoming pipeline, since pipeline always needs a trigger.
Pipeline Page
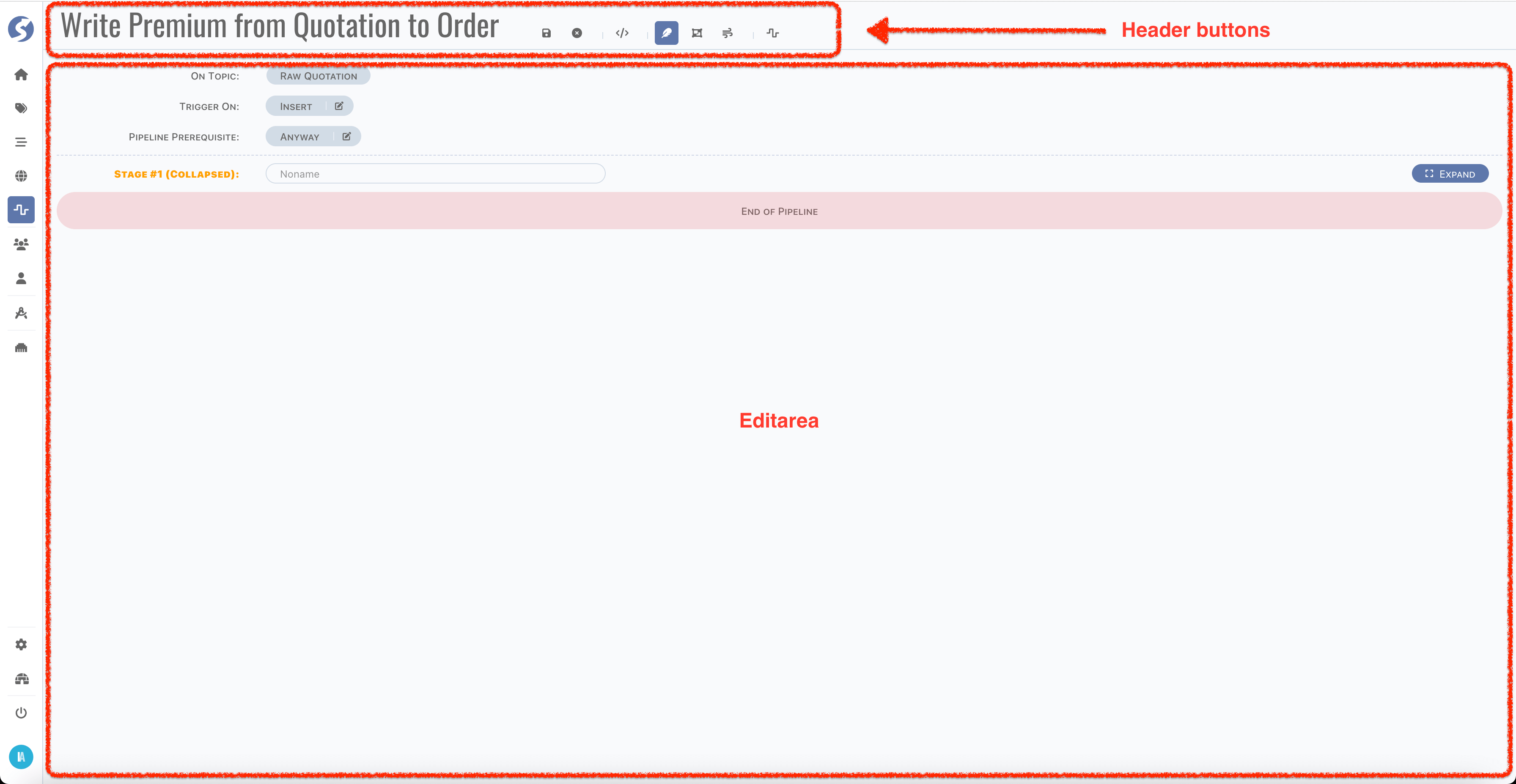
By click Open Pipeline button on topic navigator, page is switched to pipeline edit work area,
Structure of Pipeline
Before we go through the page, let's take a minute to learn the structure of pipeline.
- Each pipeline is triggered by a topic, or more accurately, by insertion/modification/deletion of a row,
- A pipeline contains multiple stages,
- A stage contains multiple units,
- A unit contains multiple actions,
- Action is the atomic execution cell.
Here is a whole picture of pipeline,
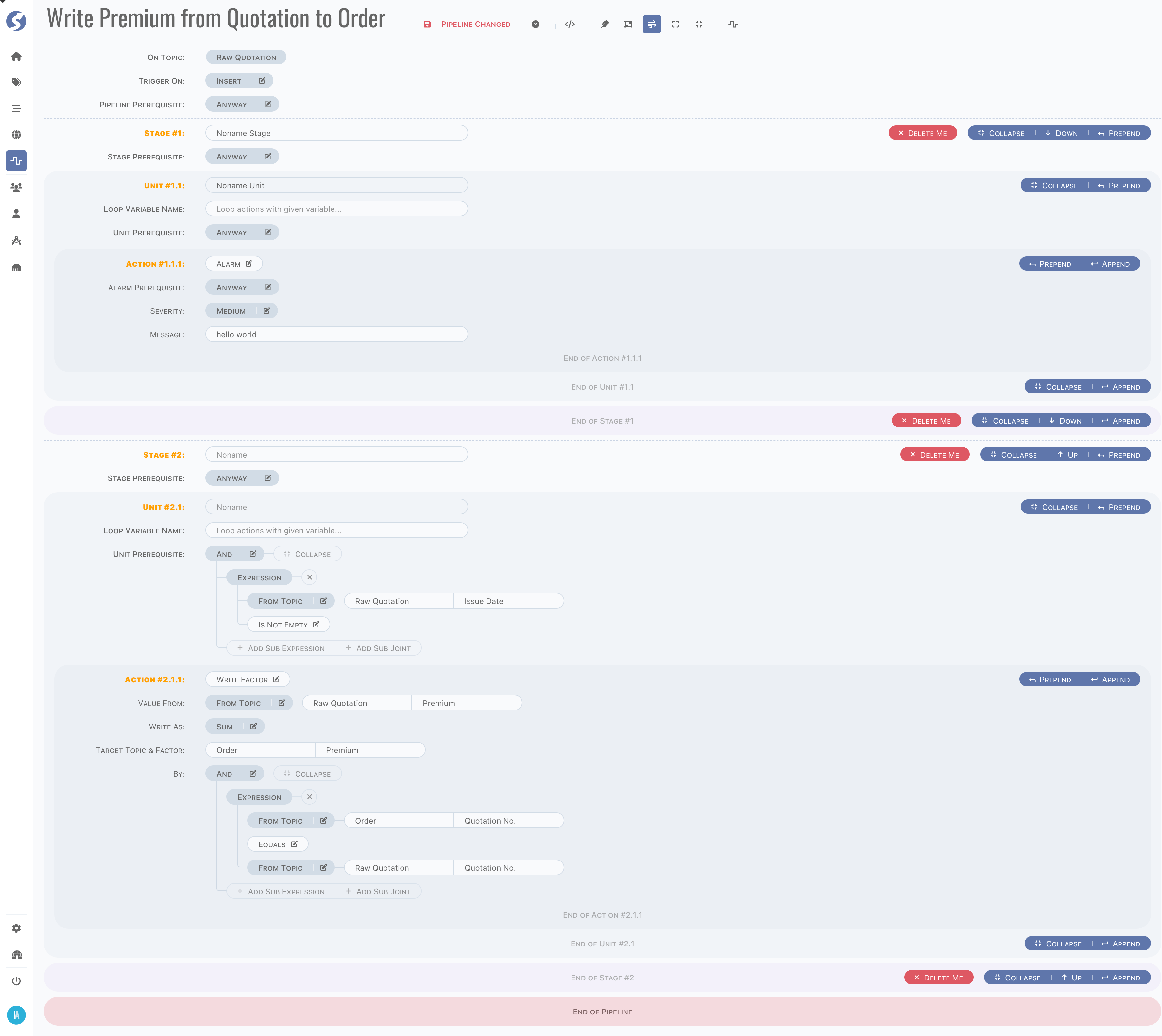
In this pipeline, there are,
- 2 stages,
- 1 unit for each stage,
- 1 action for each unit.
Header Buttons
In pipeline header,
-
Pipeline name is auto generated, click name part to change it,

-
Style of
Save Pipelinebutton is changed when anything change in pipeline, see the difference as below,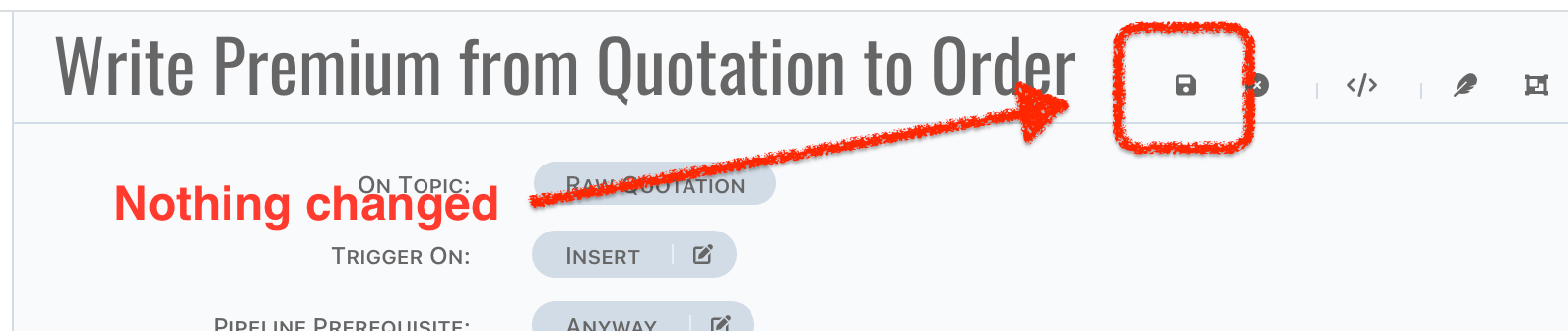
 info
infoName change will not lead the style change of
Save Pipelinebutton, it will be saved automatically, which means button style changed is caused by content of pipeline changes only. -
Pipeline can be enabled/disabled, simply click the
Enable Pipeline/Disable Pipelinebutton,
 caution
cautionEnable pipeline doesn't mean it is correct to run, we cannot know precisely it is just staged or launched. We highly recommend disabling pipelines until it is tested in simulator, and ready for environment testing.
infoContent of pipeline will also be saved when enablement switching.
-
By click the
Back to Catalogbutton, page should be switched to catalog.
Edit Modes
3 edit modes are offered,
Focus on Unit: only one unit is expanded,Focus on Stage: only on stage is expanded,Free Walk: free to expand and collapse.
Use first two modes when you are focused on part of pipeline, or use free walk to go through the whole picture.
There are 2 more buttons for free walk mode, to expand/collapse all stages.
DSL
You also can review the pipeline definition by dsl mode, it's more like a YAML.
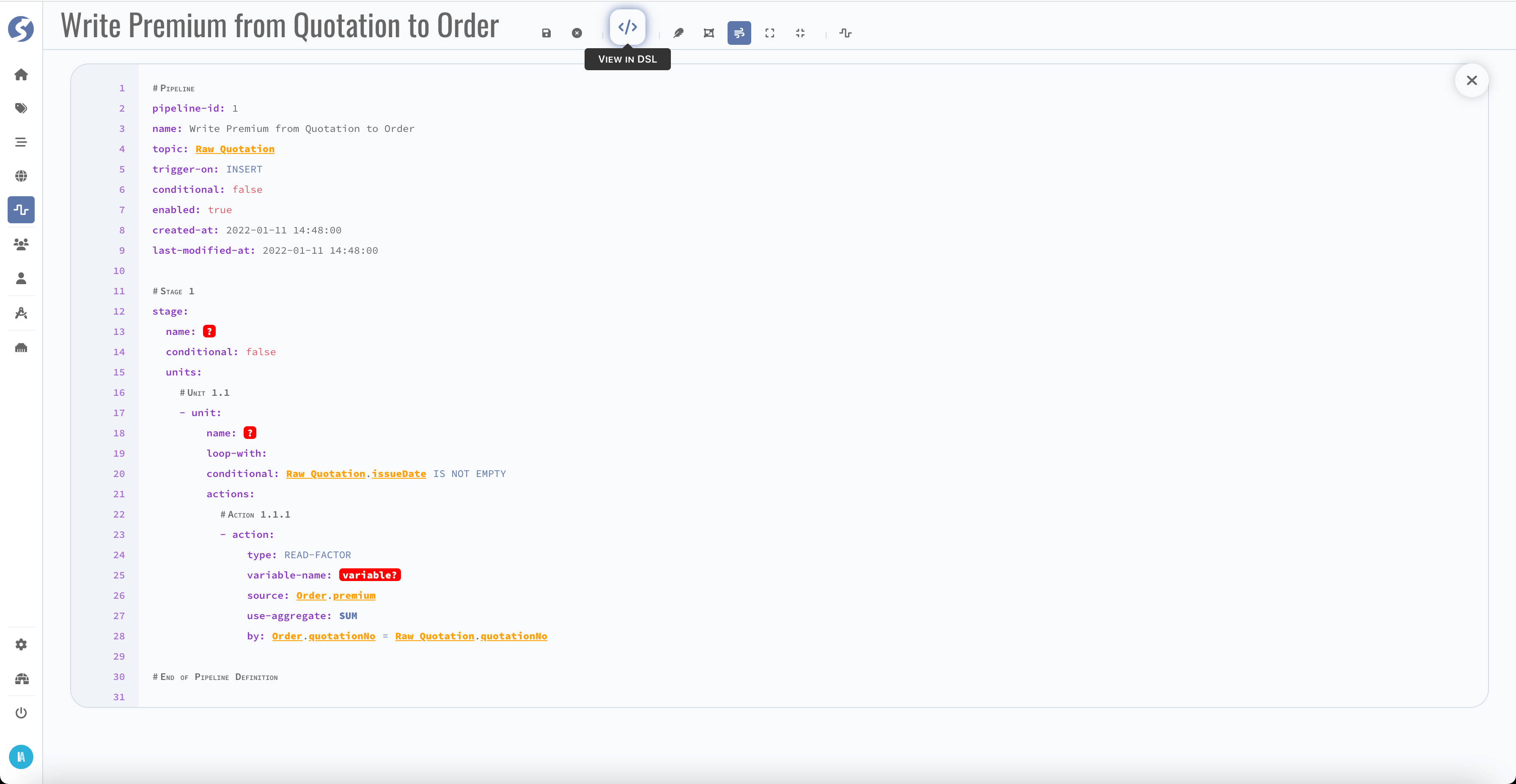
Red part means something is incorrect, check that in definition.
Define a Pipeline
In this chapter, we will introduce each part of pipeline definition.
Trigger by Topic
A pipeline is triggered by an insertion/modification/deletion of a row in topic, therefore first, a topic and how to trigger must be defined,
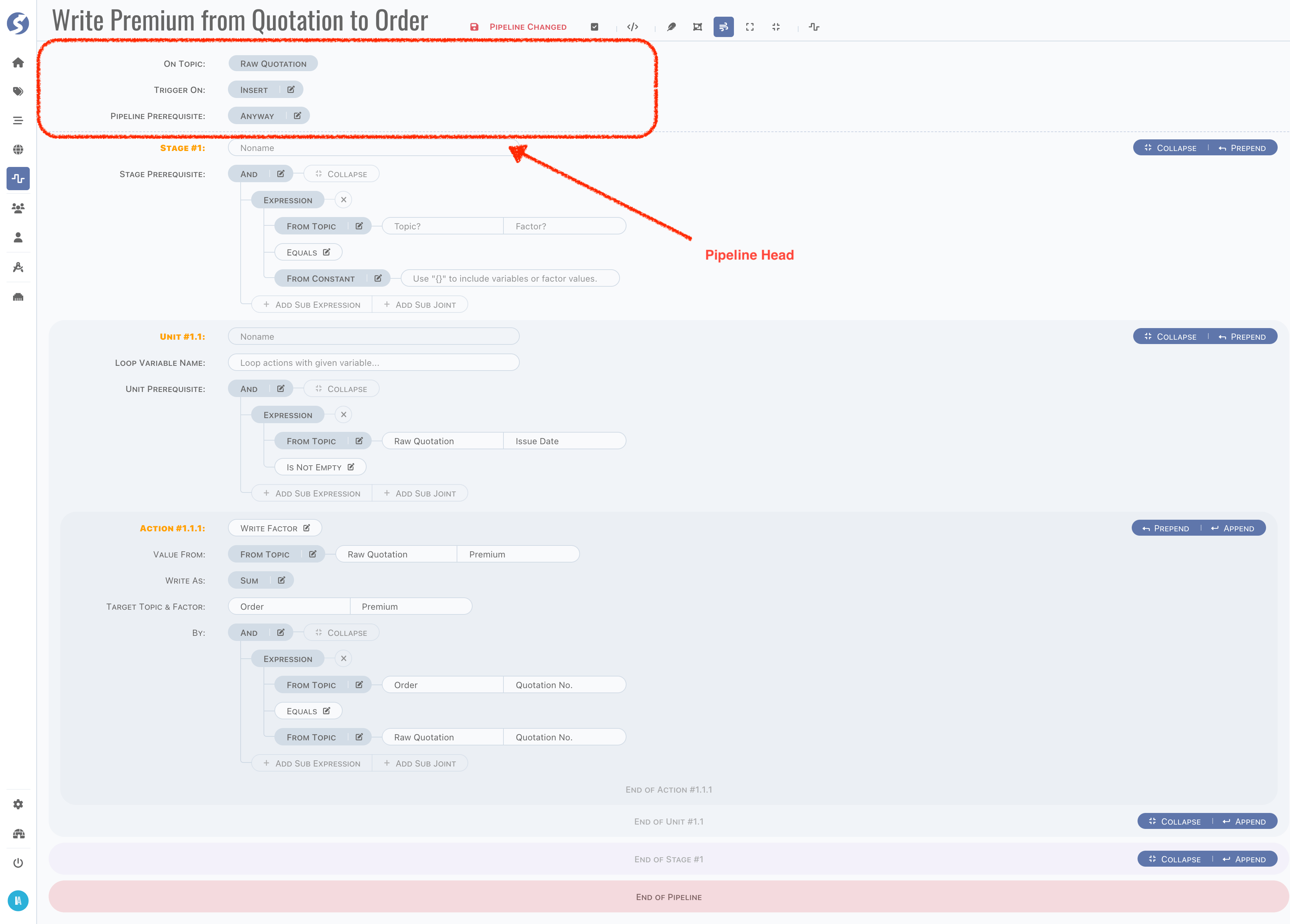
There are 4 trigger types,
- Insert,
- Insert or Merge,
- Merge,
- Delete.
Insert is usually for raw topic. For raw topics, typically only insertion occurred, each change of raw data should be recorded. For other
types of topics, Insert or Merge is a better choice, there is always a very first row was inserted, and it would be modified (in trigger
type, also known as Merge). For both of insertion and modification, the same logic should be applied. But sometimes, logics on insertion
and modification are not the same, they can be handled separately by 2 pipelines, one is triggered by Insert, the other is triggered
by Merge.
It is also supported for triggering by Delete operation, but deletion means a piece of history was removed physically. In analysis system,
each piece of data should be hold for further use, a deletion might lead a puzzle has one last piece missing, which is not expected any
time. Even it is helpful on rescuing some special situations, triggering a pipeline by deletion is still not recommended.
Sometimes logic of pipeline is very complex, hardly to define them all in one pipeline. It is possible to define multiple pipelines which
triggered by one operation. For example, there is a topic Order, an insertion occurred. All pipelines with,
- Triggerred by
Order, - Trigger type is one of
InsertorInsert or Merge,
Will be triggerred at the same time. Pipelines will be dispatched to different Doll nodes, they are run concurrently. Generally, it does not need to be concerned, but in fact, it is highly correlated with how to define pipelines. For example ( not quite fit, just for explanation), we have topics and pipelines as below,
There are several pipelines,
- Triggered by
Order,- One writes to
Order Premium, - The other writes to
Order Item(assume a set of items in an order),
- One writes to
- Triggered by
Order Item, do count aggregation, writes toOrder Item Count, - Triggered by
Order Premium,- Read count from
Order Item Count, - Compute average item premium of each order, writes to
Average Item Premium of Order.
- Read count from
Obviously, step 2 must have been done before step 3. Unfortunately, the order is unknown since pipelines are run concurrently, which means there might be a zero or null when read count in step 3.i. In this case, follow steps as below to avoid this possible problem,
- Add prerequisite on unit, to avoid the average calculation from incorrect count value,
- A
Is Not Emptycheck to avoid null, - A
Not Equalscheck to avoid zero,
- A
- Create a new pipeline from
Order Item Count, do the same logic when count changed,- Also do check to avoid null value from order premium.
Now, no matter what value comes first, the computed value in Average Item Premium of Order always is correct (or correct at that moment).
Sometimes, pipeline is defined to be performed in specific cases. For example, triggered by Order modification, according to the status of
order,
- Write to
Order Premiumin normal case, - Set premium to zero in
Order Premiumwhen status isCancelled.
Logics can be separated to 2 pipelines, and for each pipeline, performed on its prerequisite,
- For normal case, let prerequisite be
Status is not Cancelled, - For cancelled case, let prerequisite be
Status is Cancelled.
In pipeline prerequisite definition, only topic data which triggerred this pipeline can be used.
In following chapters, we will discuss how to use the old copy of trigger row. Find more details on Parameter Definition > Constant > Functions.
Stage
Pipeline includes a group of stages, stages run sequentially.
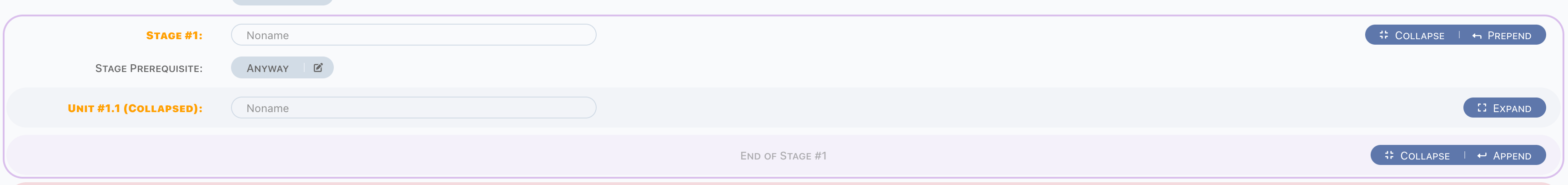
For each stage,
- Can be named,
- Has a prerequisite,
- a group of units.
In fact, stage is a group of units.
Unit
Stage includes a group of units, units run sequentially.
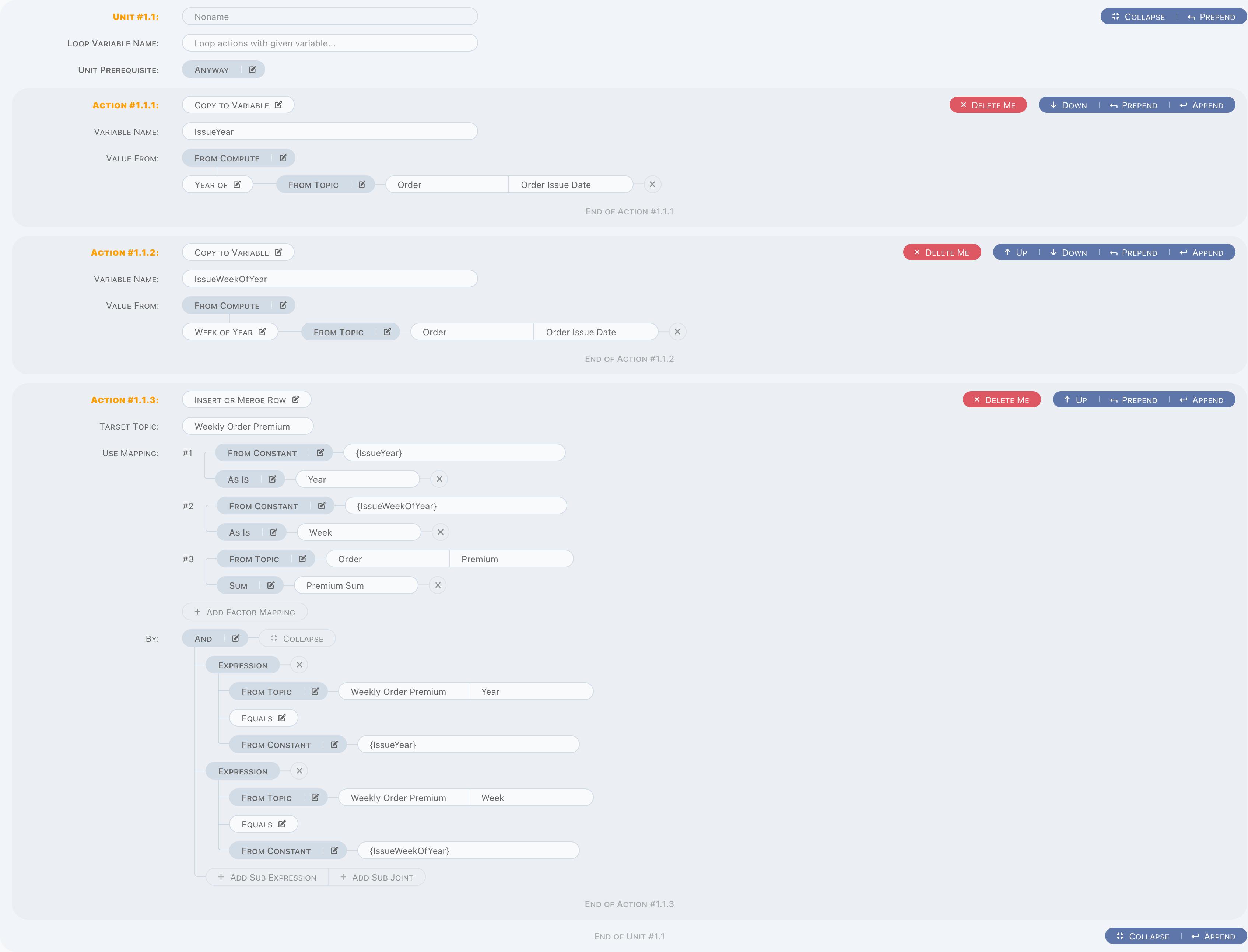
Unit is a group of actions. Normally, it is similar with stage to units, for each unit,
- Can be named,
- Has a prerequisite,
- a group of actions.
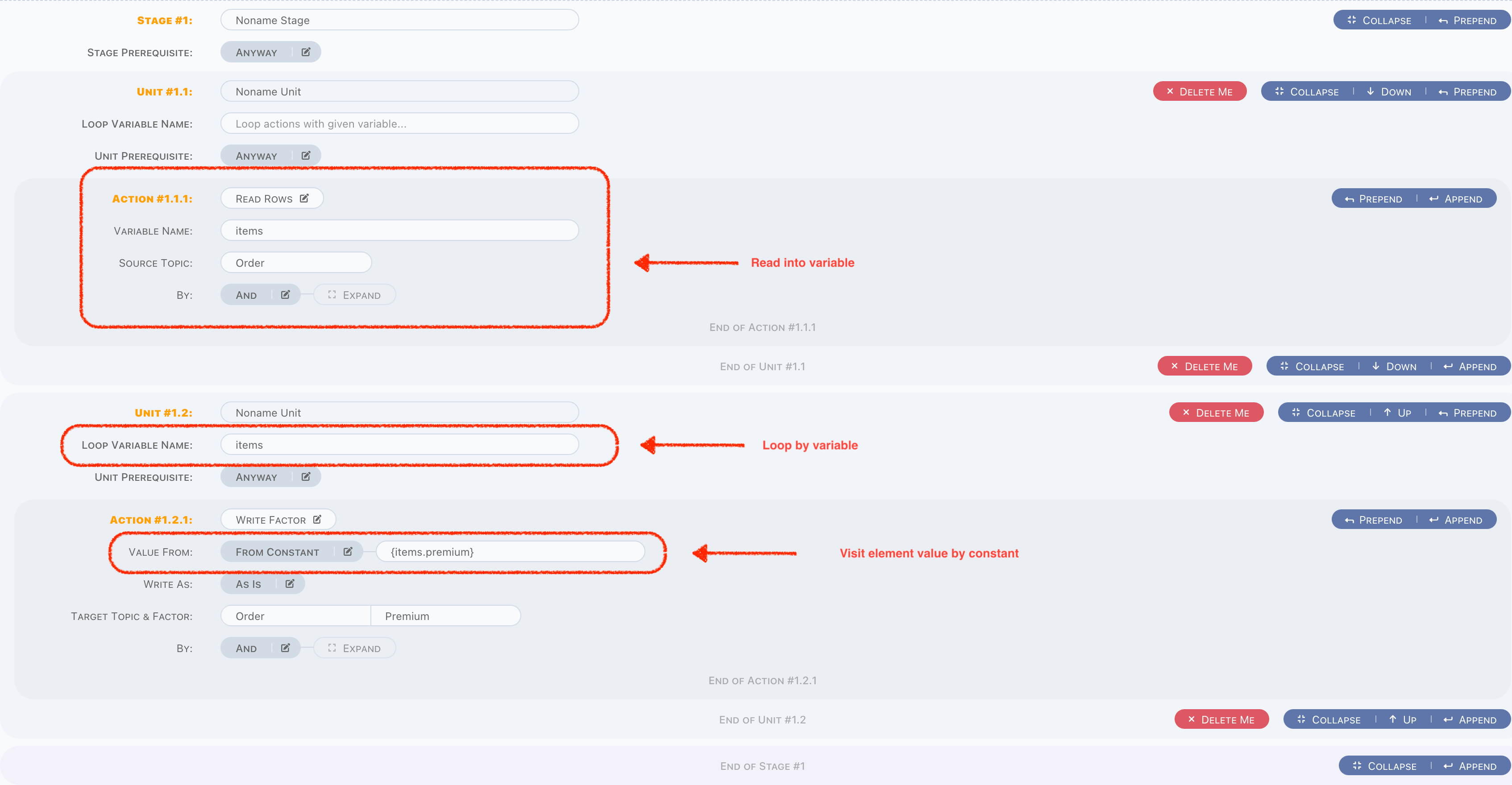
And there is a Loop Variable Name, in case of a variable is an array or a list, fill this input with variable name, then unit will run for
each element of this variable. It can be simply understood as a loop, likes a for each. Variable must be defined in previous stages or
units, otherwise runtime exception will be raised. Typically, array/list variables are from raw topic or action Read Rows/Read Factors,
and when in loop, there is a small difference with regular process, for example, we have an items variable, which got from Read Rows (
let's just ignore the read part, will discuss in actions chapter),
- Define
itemsinLoop Variable Name, so this unit will do a loop based on givenitemsdata, - Obviously, element of
itemsshould be visit in actions of this unit, simply use{items.premium}in constant parameter.
Like this,
Action
Action is the atomic part of pipeline, there are several types of action are offered for operating data or something else.
All action types as below,
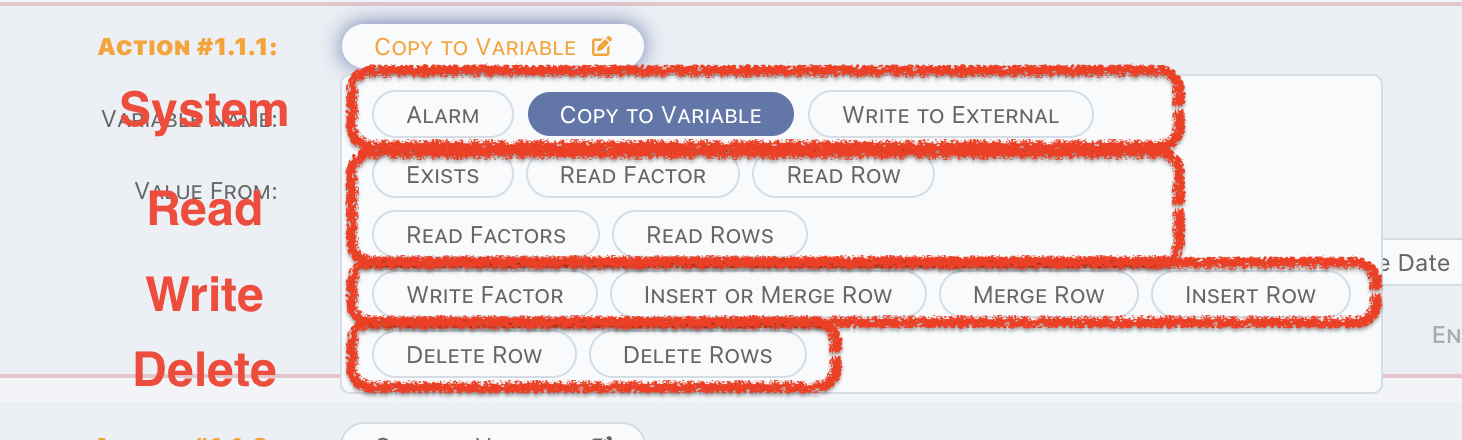
They can be categorized as three,
- System: in-memory operations,
- Read: read data from a topic,
- Write: write data to a topic,
- Delete: delete data from a topic.
Now let's go through the actions one by one.
In-Memory Actions
Alarm
Alarm is an in-memory operation, which,
- Has a prerequisite,
- A severity to categorize alarm priority,
- A message which including variables.
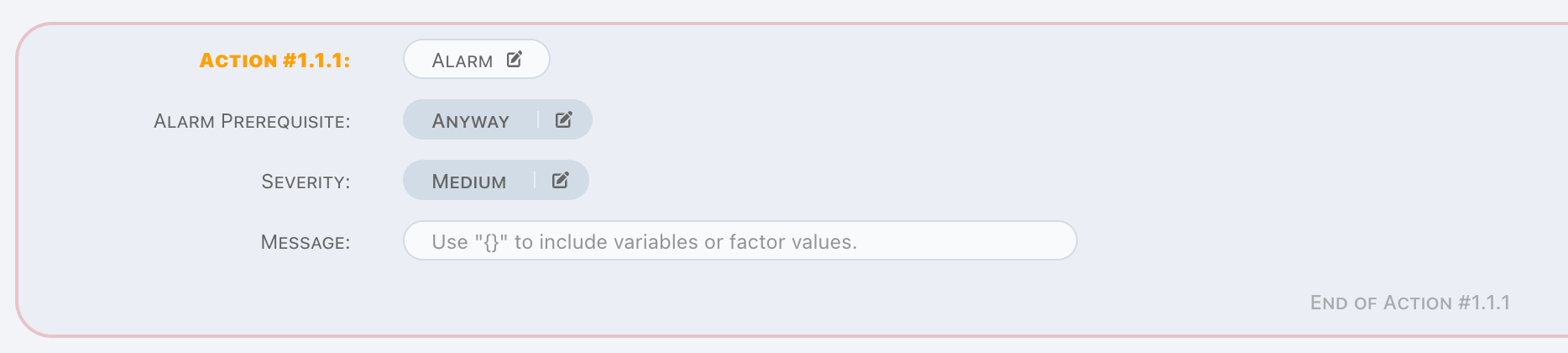
For alarm action, now there is a log message only, find Doll for more details.
Copy to Variable
Copy to Variable is an in-memory operation, a simple example as below,
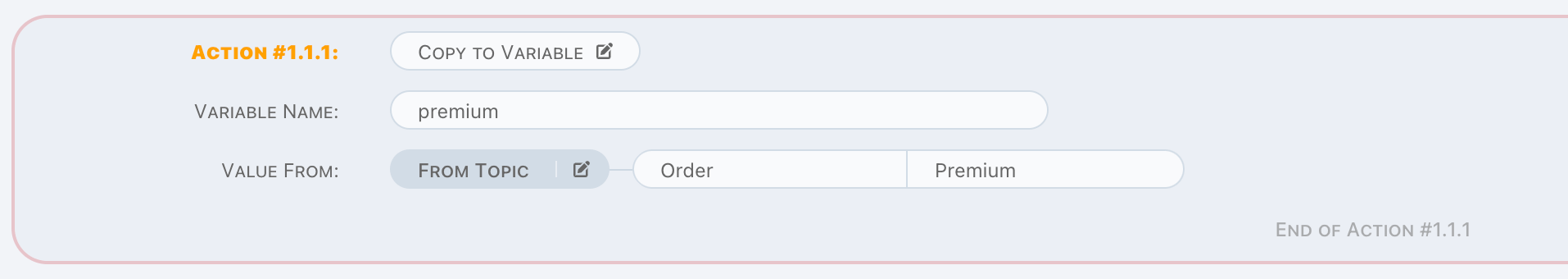
It can be used to copy
- Property value from trigger data,
- Constant value from previous variables,
- Mix above two through computed value,
to a new variable. It is helpful on preparing the data in memory before doing r/w operations, makes logic more clearly.
Only trigger topic is available in this action.
Write to External
Write to External is an in-memory operation, it is designed to write trigger data to external system.
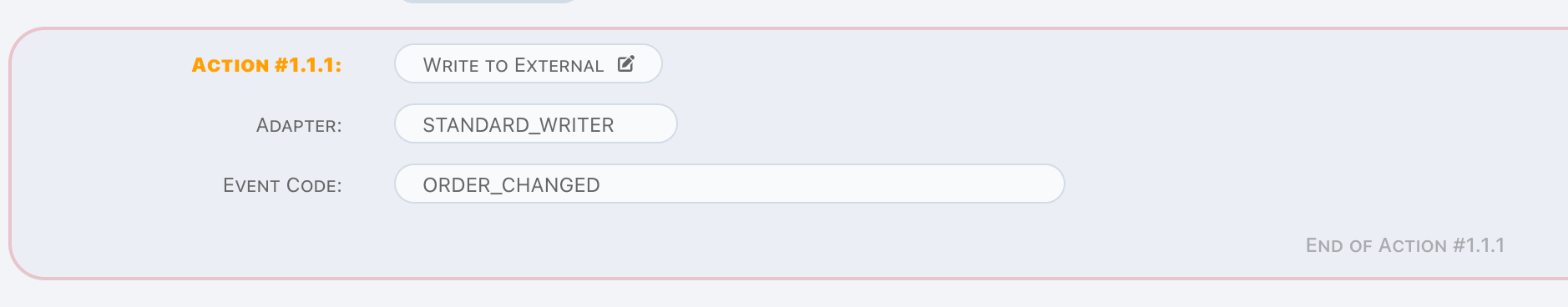
Simply choose the external writer, and assign an event code.
Here to find how to define external writers.
Pipeline engine treats external writing as a synchronous operation, any exception raised will break the pipeline. If you don't care about the status of external writing, provides an asynchronous external writer by yourself and choose it in action. Here to find for details about how to extend external writers.
Read-Data Actions
Exists
Exists is a read operation. In some cases, existing or not is the only thing we want to know instead of the exact value. Exists is
exactly designed for these situations.
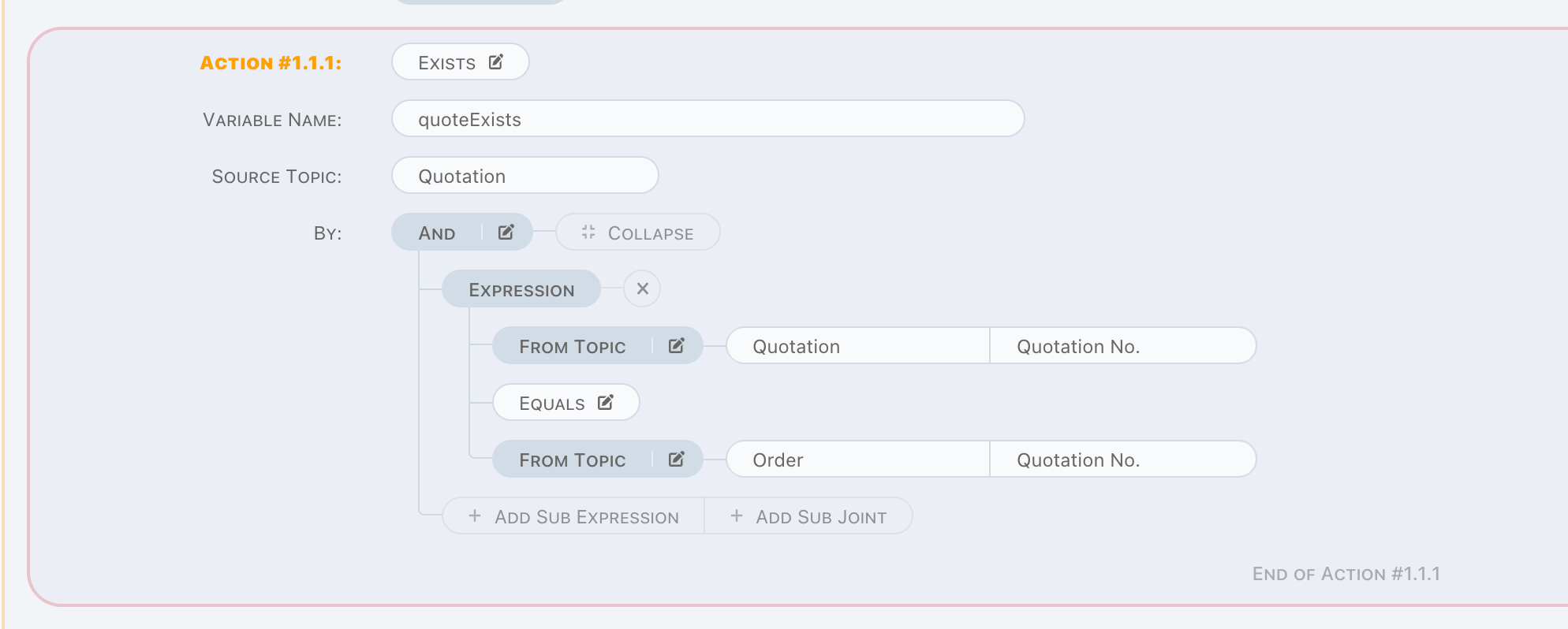
In above case, it can be understood as a simple SQL as below,
SELECT COUNT(1) FROM TOPIC_QUOTATION WHERE TOPIC_QUOTATION.QUOTATION_NO = ?;
Order is trigger topic, thus, Order.QuotationNo is in-memory, and will be passed to above sql as parameter binding value.
Exists checks count of search result, returns true when not zero, otherwise false instead.
Read Factor
To know the exact value of a factor, use Read Factor. Read Factor is a read operation.
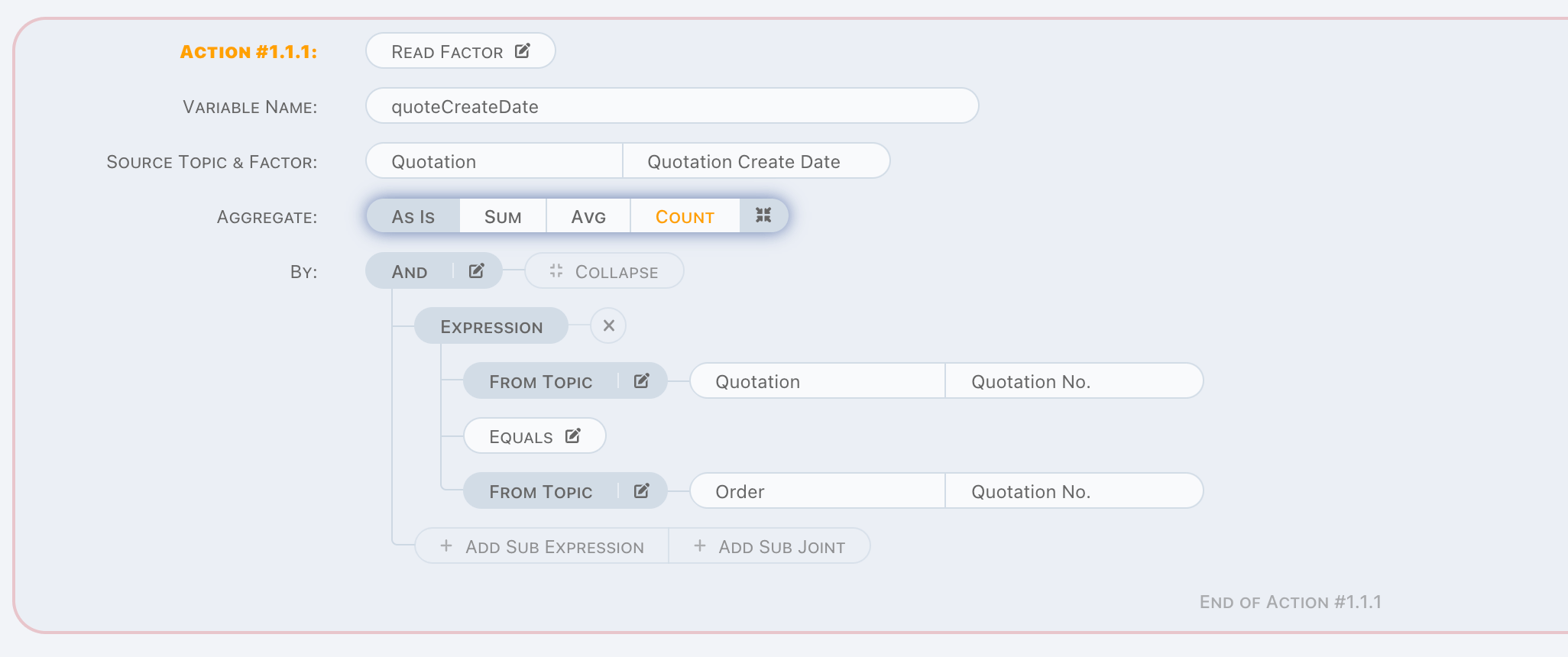
It is similar with Exists, except value will be read to variable. You can see the difference between these two actions, in Read Factor
action,
- A factor must be chosen,
- An aggregation arithmetic can be applied.
In above case, it also can be understood as a SQL as below,
SELECT TQ.QUOTATION_CREATE_DATE FROM TOPIC_QUOTATION TQ WHERE TQ.QUOTATION_NO = ?;
We use As Is in this statement, which means don't do anything more on read value, just read as what it is. But in some cases, we use
criteria to read a set of values and want to know the aggregation value of them, that's why we offer three more aggregation arithmetics
here, they are,
- SUM
- COUNT
- AVG
If COUNT is picked in above case, in SQL, it will be,
SELECT COUNT(TQ.QUOTATION_CREATE_DATE) FROM TOPIC_QUOTATION TQ WHERE TQ.QUOTATION_NO = ?;
Make sure there is one and only one row which fulfills the given criteria when aggregation is As Is, otherwise unpredicted exception might
be raised in runtime.
In watchmen, it is very important to ensure behaviour of runtime is predictable, the above situation implies uncertainty because read engine
cannot ensure the order of data, it must be swept away.
Read Factors
Read Factors is a read operation to retrieve a set of factor values.
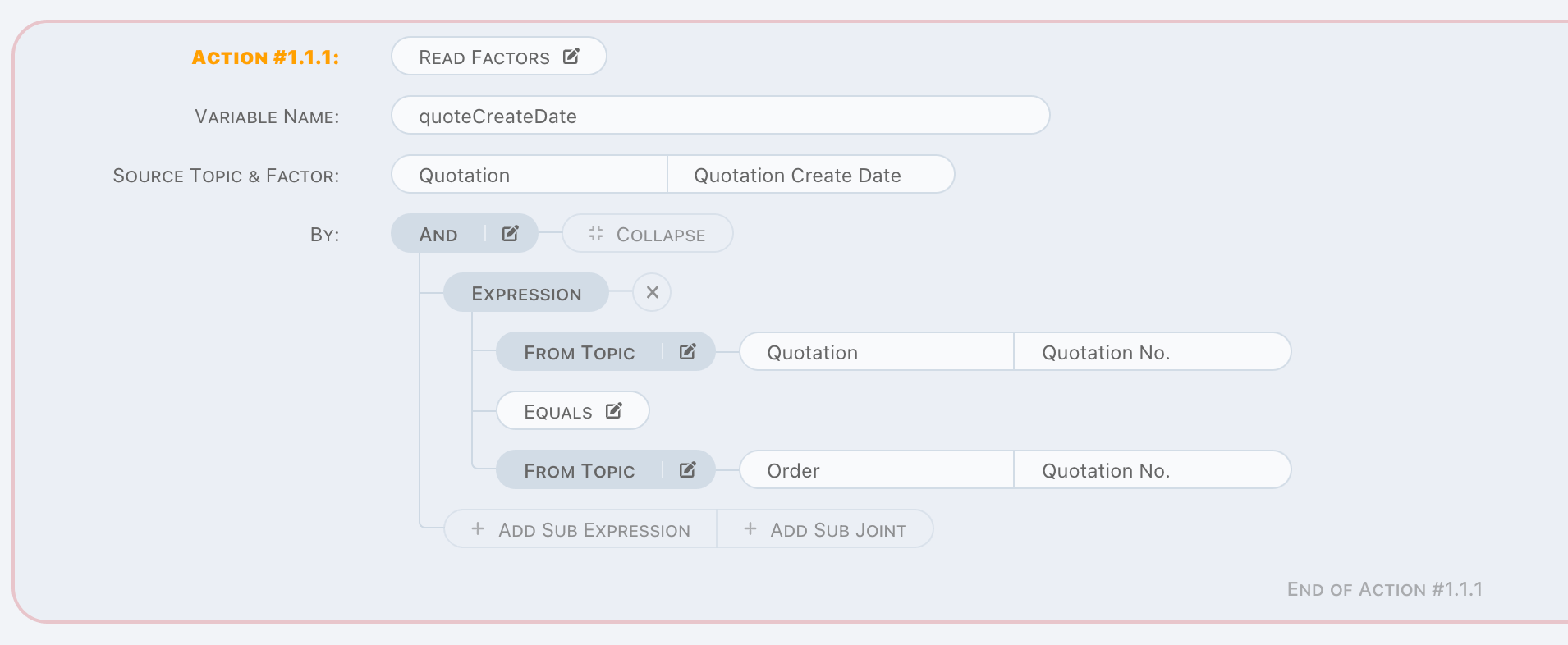
The only difference from Read Factor is no aggregation arithmetic here. Values will be read as a list into variable, and it can be used to
do a loop in next units.
Variable is a list even there is only one factor value read.
Read Row
Read Row is a read operation. Difference to Read Factor is read a row to a memory object instead of a factor value.
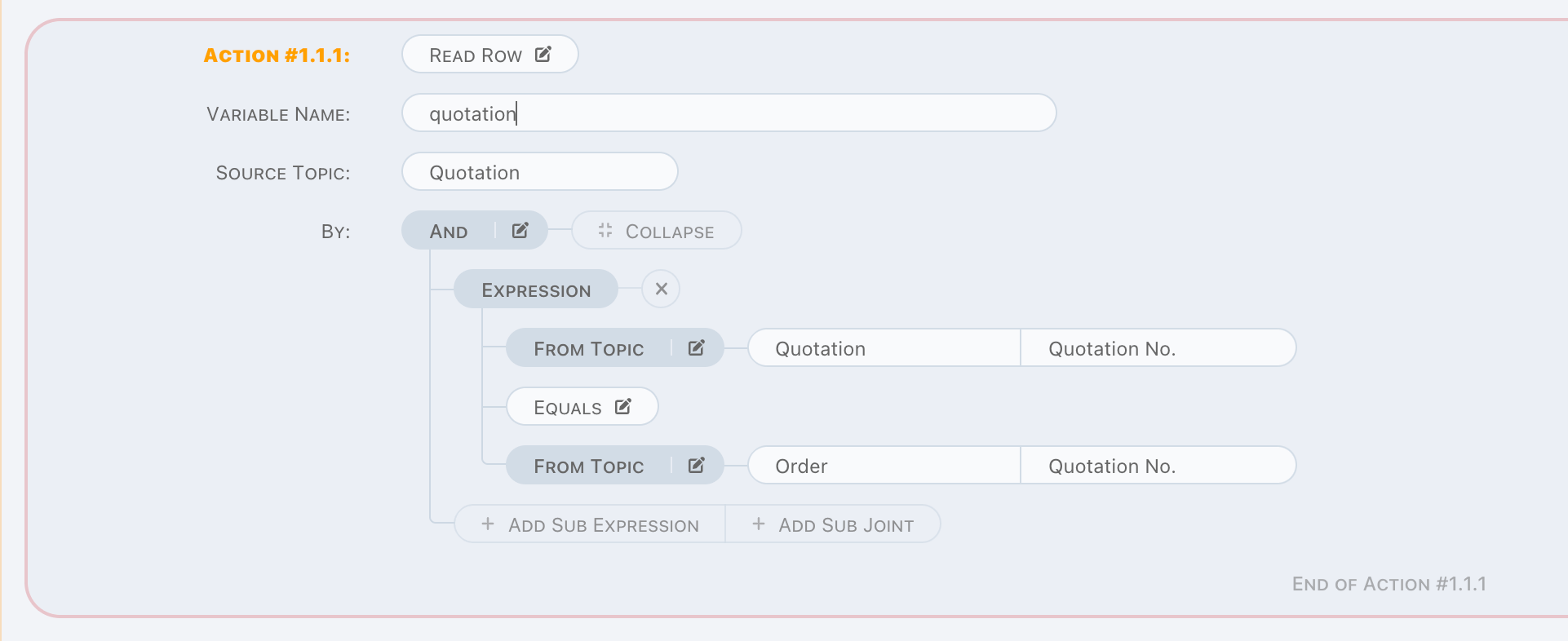
Obviously, factor and aggregation arithmetic is not needed here.
Same as As Is in read factor, one and only one assertion is very important here, we have to remove uncertainty in the first place.
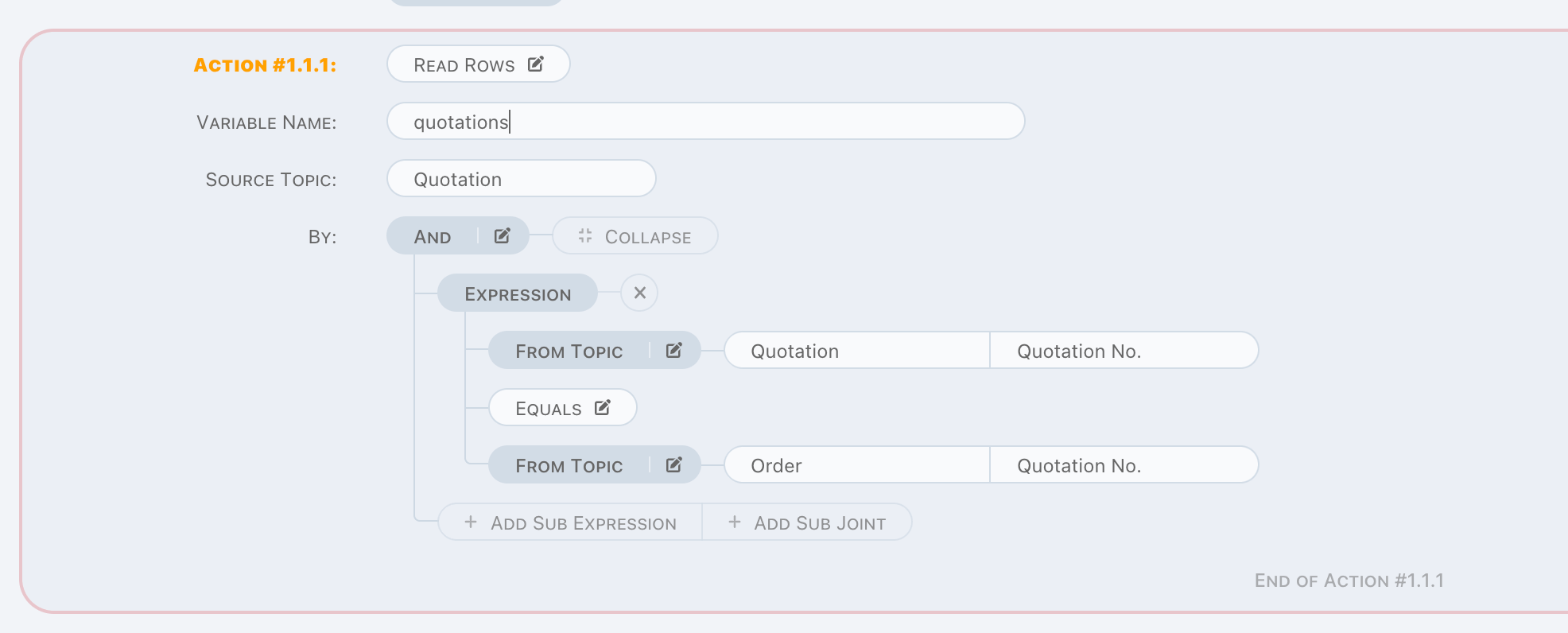
Read Rows
Read Rows is a read operation, rows matched by given criteria will be read into memory. Usually, it is used to do a loop in next unit.
Write-Data Actions
Write Factor
Write Factor is a write operation.
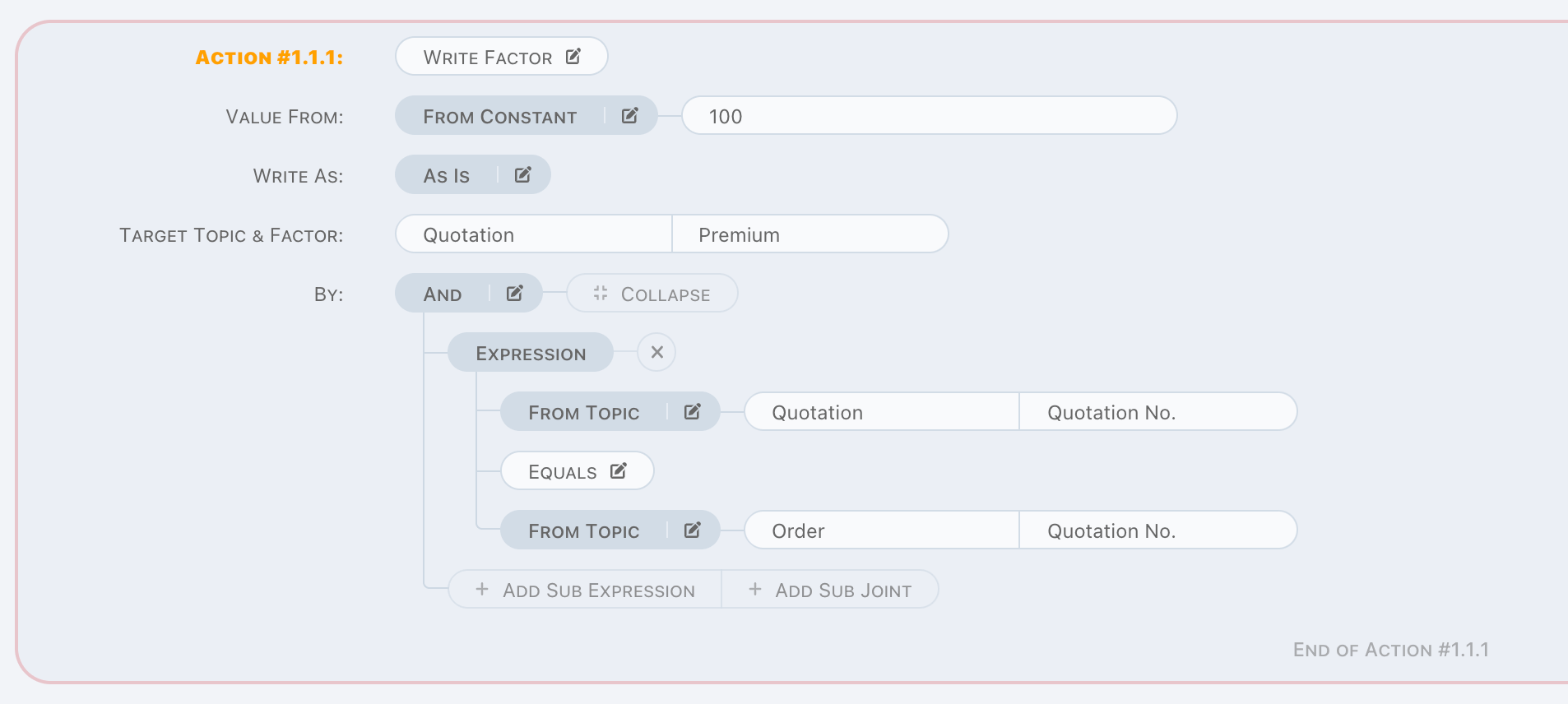
It is used to write a value to appointed factor by
- A factor of trigger data,
- A constant might contain variables,
- Mix above two through computing,
on given criteria. And when from value is a value list, it should be aggregated by aggregation arithmetic, same as Read Factor, supported
aggregation arithmetics are
SUMCOUNTAVG
Insert Row
Insert Row is a write operation.
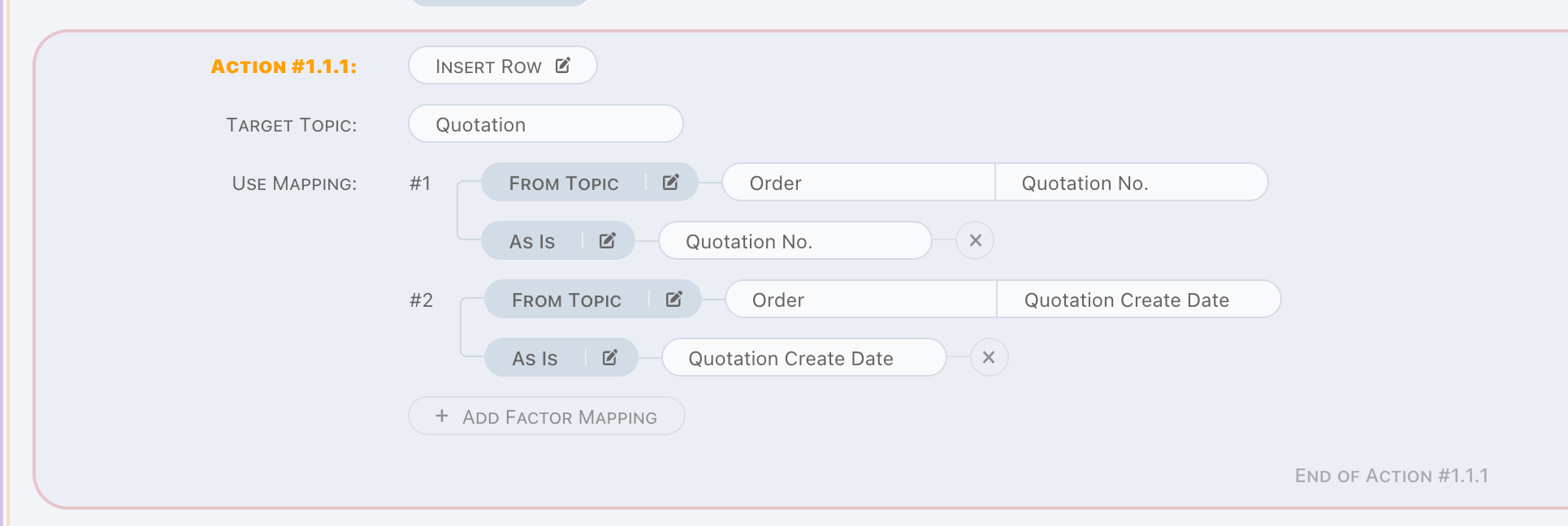
A new row will be created on appointed topic, target factors are written by appointed mapping. Each factor can be mapped independently, and aggregation is provided as well.
Any conflict causes insertion failure breaks Insert Row action, so make sure insertion can be done correctly.
Merge Row
Merge Row is a write operation.
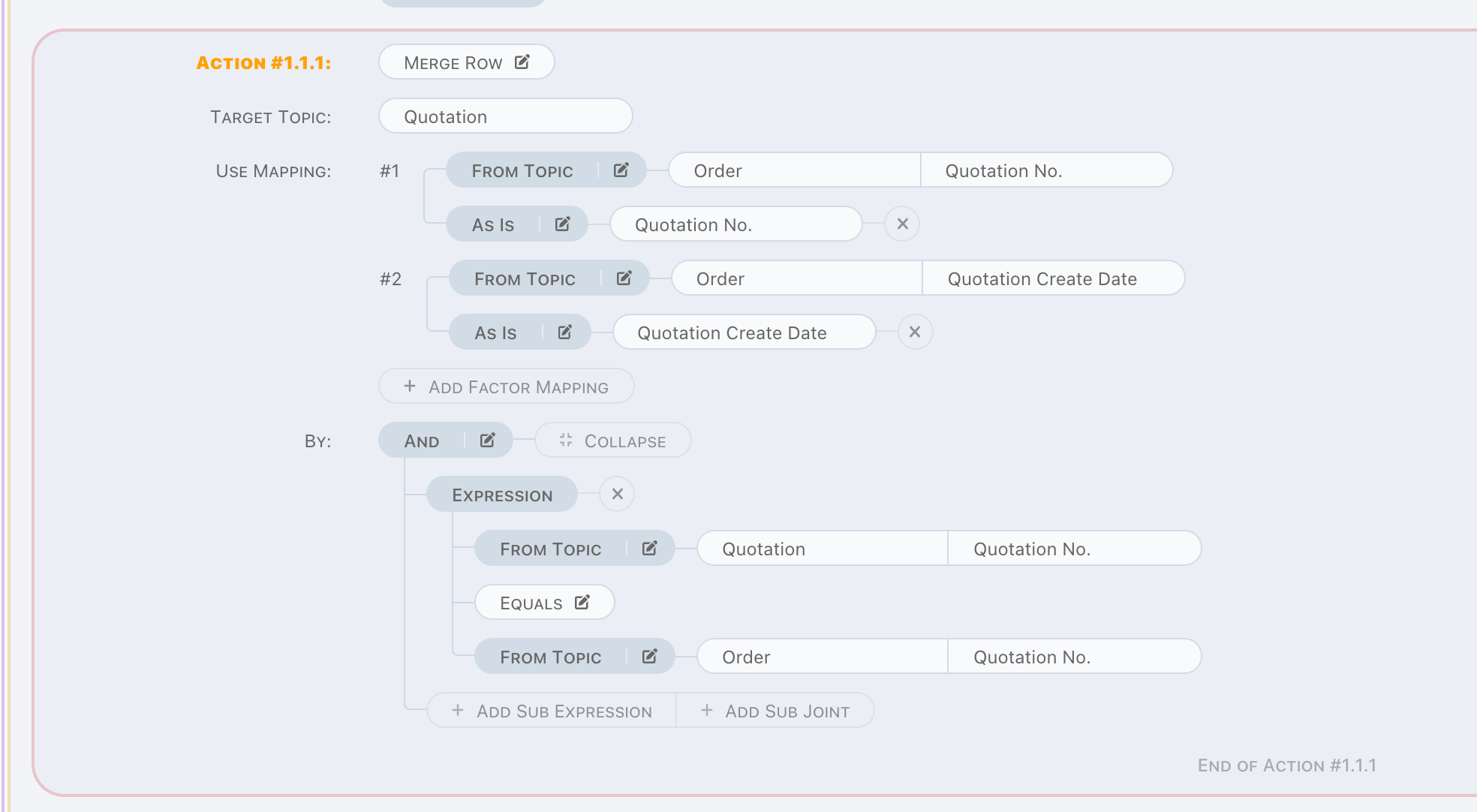
This action always do a modification on data matched by given criteria on target topic. Other parts, is the same as Insert Row.
Runtime exception raised when no data found by given criteria, so make sure data can be found.
Insert or Merge Row
Insert or Merge Row is a write operation. Actually it is a mixed version of Insert Row and Merge Row, following steps are applied in
this action,
- Find row by given criteria,
- Do a modification when found,
- Do an insertion when not found,
- Do a modification when conflict exception raised on insertion.
Delete-Data Actions
Delete Row
Delete Row is a delete operation.
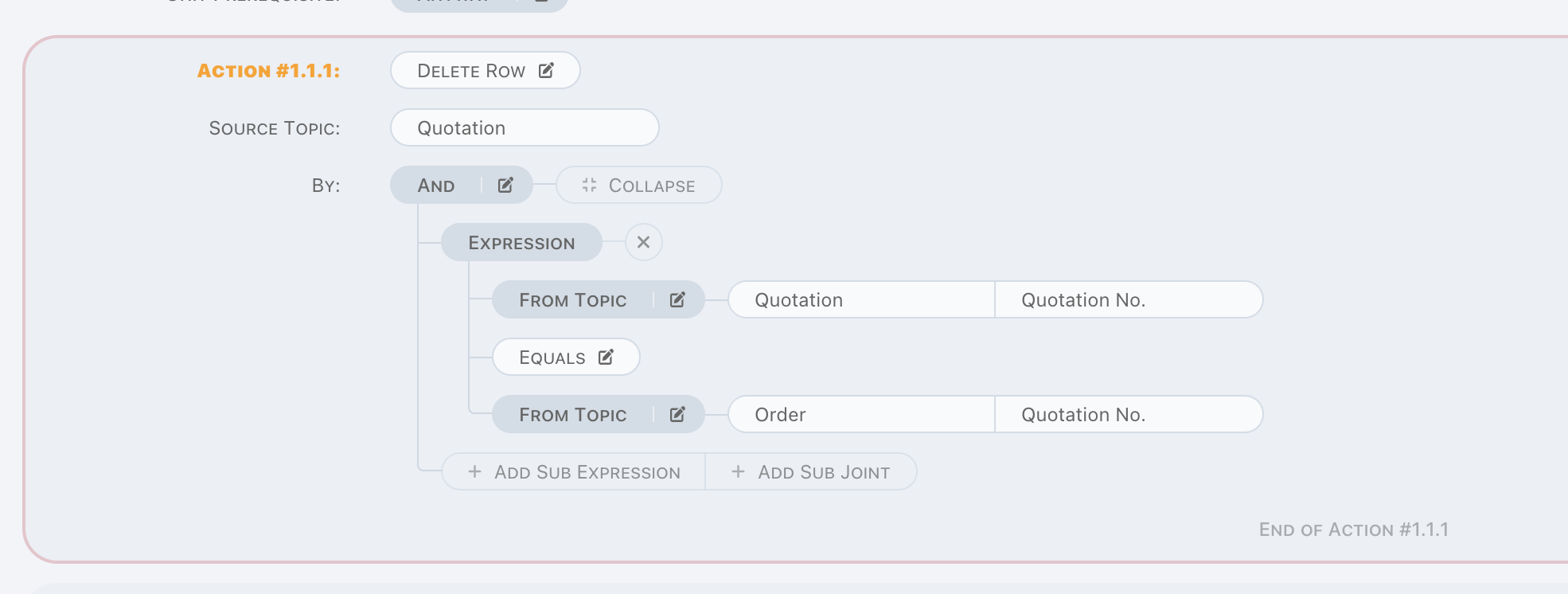
Runtime exception raised when no data found by given criteria, so make sure data can be found.
Delete Rows
Delete Rows is a delete operation for bulk data.
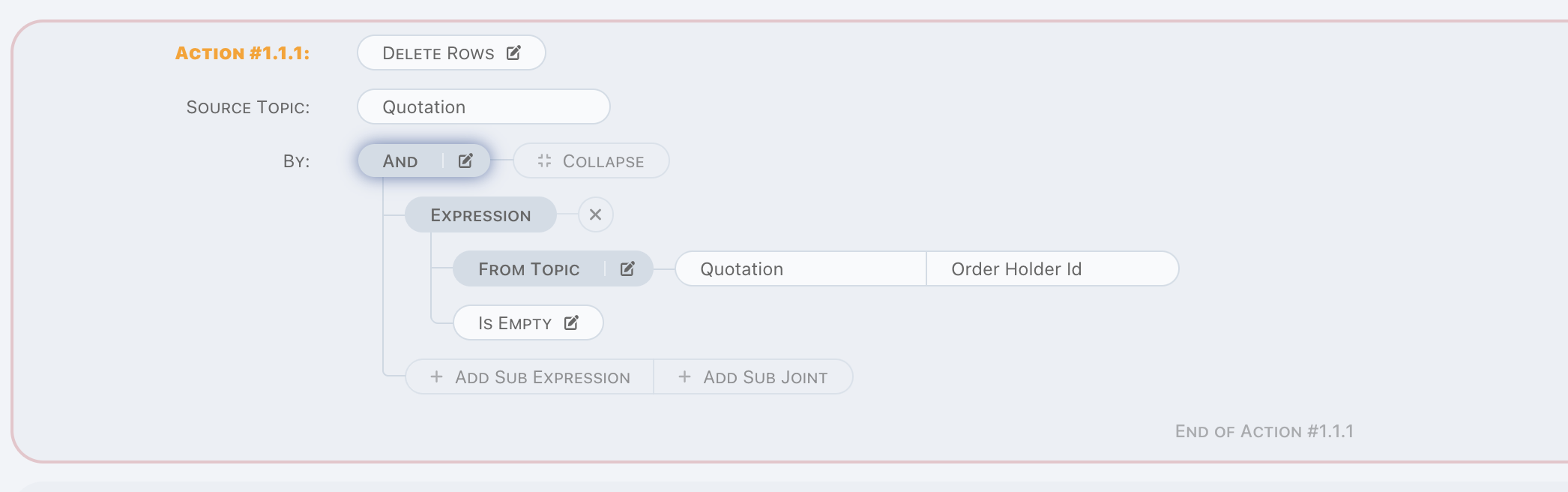
This action reads data by given criteria, and delete them one by one.
Runtime exception raised when data not found on deletion, and bulk operation is stopped.
Variables In Pipeline
Variable is a special concept in pipeline, it is designed to put some data into memory temporary. Once it is declared, it can be used in each pipeline part following. Variable value will be replaced when another declaration by same variable name, and there is no type check for variable, which means on first declaration, it can be an object, and might be a number on second declaration. Besides the replacement strategy, variable is immutable, there is no way to change variable value in memory except re-declaring.
It is much more alike with variables in RUST, immutable and explicit declaring.
Variable is visited by name, for example, visit a variable via name premium, pipeline runtime engine find value by following,
- Find the explicit declaration in previous, it is
- Declared by read actions,
- Declared by copy to variable action,
- Or find property of trigger topic when it is not found in step one.
In constant parameter, variables are declared between {}, and use . to visit sub property.
Parameter Definition
Parameter is used in
- Prerequisite of pipeline/stage/unit,
- Prerequisite of
Alarmaction, - By of read/write actions,
- Mapping of write actions.
And also, the followings can be considered as another form of parameter,
- Message of
Alarmaction, - Value from of
Copy to Variableaction, - Value from of
Write Factoraction.
There are 3 types of parameter for different purposes.
From Topic
Read from/write to topic, topics available for parameter depend on situation where parameter is. For example,
- In pipeline prerequisite, only trigger topic is available,
- In by criteria of write actions, only trigger topic and target topic are available.
Constant
Constant parameter is more flexible than topic parameter, it can be used to
- Simply define a constant value, such as a number
100, a stringHello World, - Retrieve data from variables by
{}, - Call built-in functions.
We already learned how to retrieve data from variables in actions chapters. And to define primitive constant value is just enter them in constant input, it's too simple and not worth going to detail about. Now we are going to learn the built-in functions.
Functions
Functions always starts from a character &, and also there are several categories for functions. In the following part, we will learn to
call these functions in constant parameter.
System
{&nextSeq}, to generate a sequence value,{&now}, to generate current date time,{&old.x}, to getxvalue of old data of trigger one,- Be carefully, it might be a null if pipeline is triggerred on
InsertorInsert or Merge, xis property name of trigger topic.
- Be carefully, it might be a null if pipeline is triggerred on
Ask a Value of Something
{x.&count}, to get element count of variablex,- or by
{x.y.&count}, to get count ofx.y, xis a variable,- Count is available when value is a list or an array,
- or by
{x.&length}, to get length of variablex,- or by
{x.y.&count}, to get length ofx.y, xis a variable,- Length is available when value is a string,
- or by
{x.&sum}, to get sum value of variablex,- Same as
&count, but ask sum value. - Null or empty value is summed as zero,
- Other non-numeric value leads runtime exception.
- Same as
Compute Functions
{&dayDiff(end_date, start_date)}, compute the days between given dateend_dateandstart_date,{&monthDiff(end_date, start_date)}, compute the months between given dateend_dateandstart_date,{&yearDiff(end_date, start_date)}, compute the years between given dateend_dateandstart_date,
In above cases, end_date/start_date are variables. In another hand, &now also can be one of the parameter.
-
{&fmtDate(date, format)}, format the given datedate. The following table describes the format specifiers:Specifier Description Y Year, numeric, four digits y Year, numeric (two digits) M Month, numeric (01 .. 12) D Day of the month, numeric (01 .. 31) h Hour (00 .. 23) H Hour (01 .. 12) m Minutes, numeric (00 .. 59) s Seconds (00 .. 59) W Weekday name (Sunday .. Saturday) w Abbreviated weekday name (Sun .. Sat) B Month name (January .. December) b Abbreviated month name (Jan .. Dec) p AM or PM
&factor_name is also available in above functions, in find by definition only, factor must be defined on source or target topic.
Computed
Computed parameter is mixed version of constant and topic parameter. In the meantime, it also can be part of another computed one. There are several built-in functions,
- Math:
Add,Subtract,Multiply,DivideandModulus, - Date:
Year Of,Half Year Of,Quarter Of,Month Of,Week of Year,Week of Month,Day of MonthandDay of Week, - Case When, which also is known as
- A
switchin Typescript, - A
pattern matchin Python, - Or a
if, else if, elsein Java, - etc.
- A
Validation
We try to do a full validation with pipeline, but since many of them are based runtime data, which means they cannot be validated on design time. According to this, we do not list the validation rules here. Pass the validation is a beginning of pipeline definition, it is highly recommended that check the defined logic carefully, and test it in simulator before applied it to environment.